Table of Contents


Want to Boost Rankings?
Get a proposal along with expert advice and insights on the right SEO strategy to grow your business!
Get Started
In a recent discussion on LinkedIn, Google Analyst Garry Illyes emphasized the importance of disallowing action URLs, such as “add to cart” and “add to wishlist,” in your robots.txt file.
According to Garry, websites that disallow such links from getting crawled sees improved resource allocation while crawling and helps reduce server load.
Free SEO Audit: Uncover Hidden SEO Opportunities Before Your Competitors Do
Gain early access to a tailored SEO audit that reveals untapped SEO opportunities and gaps in your website.

What Happened?

Garry highlighted that action URLs should be disallowed from being crawled by search engines. These URLs include functions like adding items to a cart or wishlist, which are unnecessary for search indexing.
While Garry says website owners and SEO professionals can implement these recommendations to improve their site’s efficiency and avoid unnecessary server strain, we have heard from multiple sources that Google has significantly reduced the crawl budget for websites.
Now, it’s clear that Google has been working on reducing unnecessary crawl attempts to make the web more efficient. By encouraging webmasters to disallow non-essential URLs, Google aims to conserve resources and improve the overall performance of its search engine.
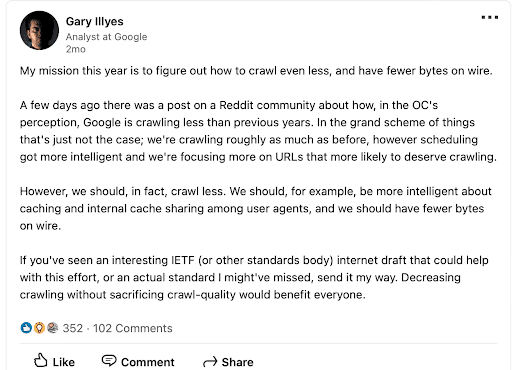
Garry had earlier written on LinkedIn: “My mission this year is to figure out how to crawl even less, and have fewer bytes on wire.
A few days ago there was a post on a Reddit community about how, in the OC’s perception, Google is crawling less than previous years. In the grand scheme of things that’s just not the case; we’re crawling roughly as much as before, however scheduling got more intelligent and we’re focusing more on URLs that are more likely to deserve crawling.
However, we should, in fact, crawl less. We should, for example, be more intelligent about caching and internal cache sharing among user agents, and we should have fewer bytes on wire.
If you’ve seen an interesting IETF (or other standards body) internet draft that could help with this effort, or an actual standard I might’ve missed, send it my way. Decreasing crawling without sacrificing crawl-quality would benefit everyone.”
Key Facts and Figures:
- Action URLs like https://example.com/product/scented-candle-v1?add_to_cart can unnecessarily consume server resources when crawled.
- Disallowing these URLs can prevent excessive crawling and optimize site performance.
Short-term and Long-term Impacts:
- Short-term: Immediate reduction in server load and improved site performance.
- Long-term: Enhanced user experience and better resource management for website owners.
For websites and SEO professionals, managing crawling directives in the robots.txt file can lead to more efficient indexing and better overall site health.
In the past, webmasters have faced issues with excessive crawling that have led to significant server slowdowns and performance issues.
Effectively managing crawler access through robots.txt has proven effective in mitigating such issues.
The current emphasis on disallowing action URLs reflects ongoing efforts to optimize search engine interactions with websites.
In future updates to crawling practices, Google may further refine how it interacts with dynamic and action-oriented content.
Since Webmasters and digital marketers want to mostly align with the recommendations of Google rather than go against it, they are likely to adopt these practices to enhance site performance and user experience.
Recommendations From Stan Ventures on What You Should Do Next:
- Update your robots.txt file: Add disallow rules for action URLs.
- Monitor crawling activity: Use Google Search Console to track crawler behavior.
- Optimize site performance: Regularly review and update crawling directives.
Tips and Best Practices
- Avoid using “nofollow” for internal links to action URLs if robots.txt rules are in place.
- Alternatively, Some search engine crawlers primarily follow and index GET requests. By converting action URLs to use POST, you reduce the likelihood that these URLs will be crawled, as many crawlers are less likely to perform POST requests due to their potential to change server state or execute actions.
About the author
Share this article
Find out WHAT stops Google from ranking your website
We’ll have our SEO specialists analyze your website—and tell you what could be slowing down your organic growth.














