Table of Contents


Want to Boost Rankings?
Get a proposal along with expert advice and insights on the right SEO strategy to grow your business!
Get StartedGoogle has officially added Google NotebookLM to its list of user-triggered fetchers, meaning the AI research assistant can now request URLs provided by users, strengthening its integration with Google’s broader ecosystem.
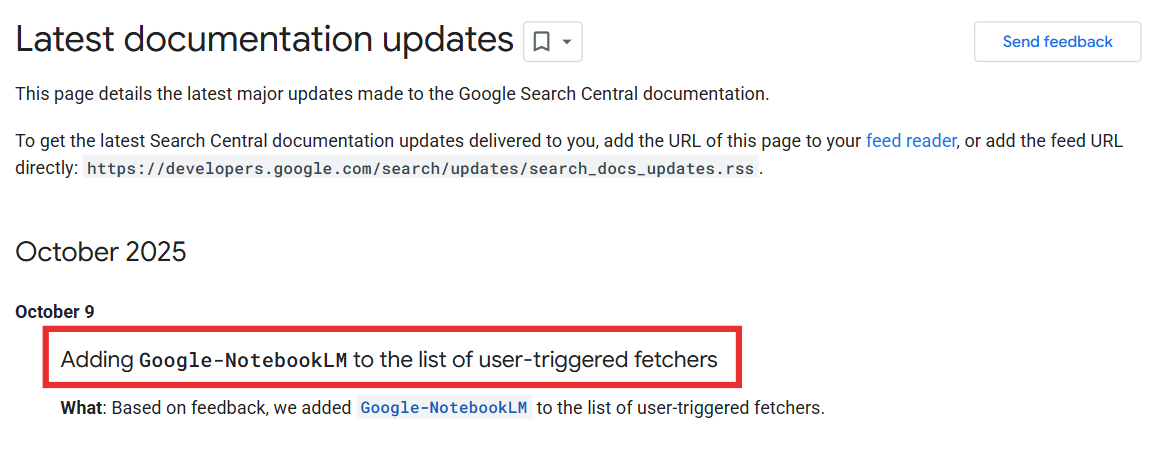
This week, Google confirmed that its experimental AI research tool, NotebookLM, has been added to the list of user-triggered fetchers, the internal category for systems that access web content at the direct request of a user.
The update came after “feedback,” according to Google’s public documentation.
Free SEO Audit: Uncover Hidden SEO Opportunities Before Your Competitors Do
Gain early access to a tailored SEO audit that reveals untapped SEO opportunities and gaps in your website.

For context, Google’s user-triggered fetchers include services like Google Site Verifier and PageSpeed Insights, tools that send fetch requests to websites not for indexing or ranking purposes, but because a user specifically asked Google to retrieve that data.
So what does this mean in practice?
If you’re a website owner, NotebookLM may now appear in your logs when a user uses it to analyze or reference content from your site.
The tool fetches URLs that users provide as sources for their personal projects, ensuring the data comes directly from those specified locations rather than from Google’s general index.
What Is NotebookLM?
Originally launched as a research project, NotebookLM is an AI-driven note-taking and research assistant powered by Google’s large language models.
It helps users summarize documents, create outlines, and draw insights from multiple sources. Think of it as a personal research companion that works with your uploaded files, notes, and links.
Why This Matters for Developers and Site Owners
While the update might sound minor, it carries meaningful implications for developers, researchers, and content creators.
Transparency in web crawling is critical, especially as AI tools increasingly interact with online data. Understanding how Google’s crawlers identify themselves, such as through the Googlebot user-agent string, helps site owners recognize legitimate activity and maintain better control over access.
By naming and describing NotebookLM’s behavior publicly, Google avoids the confusion that can arise when unfamiliar bots appear in server logs.
Site owners can now identify NotebookLM requests easily and verify that those fetches originate from user-triggered activity, not automated indexing.
This update also suggests Google’s intention to normalize AI-driven content interaction as part of its ecosystem.
NotebookLM’s fetching mechanism reflects how AI tools are evolving, less about sweeping the web for information, more about gathering user-chosen material for analysis.
How It Works: The Fetching Process Explained
When a NotebookLM user adds a link to their project, the tool sends a fetch request through the Google-NotebookLM user agent.
The system retrieves the content from that URL, allowing the AI model to summarize, cite, and synthesize it alongside other provided sources.
According to Google’s official crawler documentation, such requests are made “based on feedback” and limited to user-specified content.
The fetcher retrieves “individual URLs that NotebookLM users have provided as sources for their projects,” ensuring that control stays in the user’s hands.
This design helps reinforce Google’s stated commitment to transparency in its AI experiments. Unlike standard crawlers such as Googlebot, NotebookLM’s agent operates only within a clear, user-driven boundary.
A Step Toward AI Research Integration
Google’s decision to list NotebookLM among its official fetchers highlights a clear direction for the product. The company is building a bridge between its AI assistant and live information on the web, allowing users to work with current, verifiable sources instead of static uploads.
Researchers could use it to reference primary materials directly from trusted sites and summarize their findings in one place.
Journalists might gather quotes, citations, and background data without leaving their notes.
Students could collect readings, highlight key ideas, and generate outlines, all within a single workspace.
Granting NotebookLM an identifiable fetcher status also reinforces accountability.
Every request is traceable, and each source interaction is transparent. It shows that Google wants NotebookLM to grow into a research tool that respects both creators and users while staying grounded in trustworthy, verifiable content
Why Transparency Matters
AI systems that retrieve or summarize content from the web operate at the crossroads of creativity, copyright, and trust. Google demonstrates responsible data handling by ensuring NotebookLM only fetches data upon user request, establishing a precedent for informed consent in AI data retrieval.
This transparency can reduce friction between website owners and AI developers, especially amid ongoing concerns regarding data utilization and intellectual property rights.
Clear explanations of who is fetching data, what is being fetched, and the reasons behind it foster greater trust.
What This Signals for AI Development
This update also signals a subtle but telling trend in AI development.
As AI assistants become more capable of working with real-time sources, developers will need clear frameworks for responsible data fetching and attribution. Google’s move aligns with growing calls for openness in how AI systems access and process web content.
It’s a sign that large tech companies are beginning to codify AI behaviors within the same governance structures that oversee traditional search tools. That’s a healthy direction for the web, and for the people building within it.
Actionable Insights for Site Owners
If you manage a website, here’s what you can do:
- Check your server logs. Look for requests from the “Google-NotebookLM” user agent. These are legitimate, user-triggered requests.
- Review your robots.txt. Ensure your fetch permissions align with how you want tools like NotebookLM to interact with your content.
- Understand fetch behavior. NotebookLM requests occur only when a user explicitly provides your link to the system. It doesn’t crawl your site automatically.
- Monitor for misuse. If you notice abnormal fetch patterns, report them through Google’s support channels.
- Stay informed. Google updates its crawler list periodically. Keeping track of those changes helps you manage how AI systems interact with your content.
The Broader Picture
Though NotebookLM’s AI fetcher may appear to be a minor update, it marks a notable step in how AI integrates with online data systems.
Google’s choice to clearly identify the tool underscores a commitment to transparency, ensuring that as AI becomes more embedded in digital workflows, trust remains part of the foundation.
Key Takeaways
- Google added NotebookLM to its list of user-triggered fetchers, meaning it fetches web content only when a user provides a specific URL.
- The move improves transparency by helping web administrators recognize legitimate AI-related fetch requests.
- NotebookLM is a user-focused AI research assistant, now officially interacting with online content under user control.
- Developers and site owners can manage fetch behavior through standard web controls like robots.txt.
- The change reflects Google’s effort to integrate AI tools responsibly within its broader ecosystem.
About the author
Share this article
Find out WHAT stops Google from ranking your website
We’ll have our SEO specialists analyze your website—and tell you what could be slowing down your organic growth.














