New research shows that when websites lose visibility in Google Search, they also lose citations across AI search platforms, including ChatGPT, revealing how deeply AI answers still depend on traditional rankings.
In mid-January 2026, an unconfirmed Google algorithm update caused sharp organic visibility declines across dozens of major websites. While the initial impact appeared to be limited to traditional search results, new analysis indicates the consequences extend much further.
According to a study published by Lily Ray, drops in Google rankings are closely followed by losses in AI search citations.
The research examined whether reduced organic visibility also affects how frequently sites are referenced by AI-driven tools such as Google AI Mode, ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
Are AI search citations affected by drops in organic search?
I dug in a bit with some recent examples try to find the answer.
Check it out at my Substack:https://t.co/JBgyIVp40w pic.twitter.com/CLNUvu0mII
— Lily Ray 😏 (@lilyraynyc) February 17, 2026
The findings suggest that AI search does not operate independently of Google’s ranking systems. Instead, AI visibility appears to move in lockstep with organic search performance.
How the Study Was Conducted
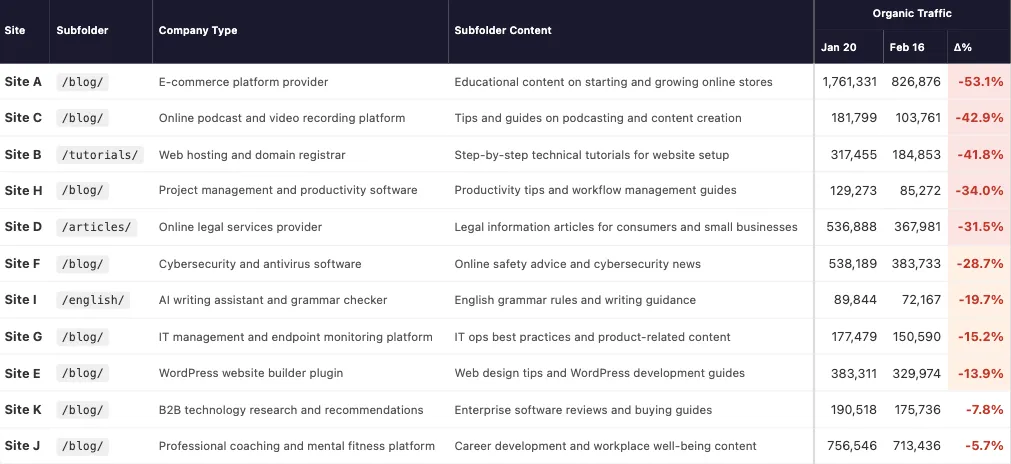
Ray analyzed 11 websites that experienced severe organic declines between January 20 and February 16, 2026.
In nearly every case, the impact was concentrated in blog or resource subfolders that previously generated informational traffic. To protect confidentiality, site names were anonymized.
Organic traffic estimates were pulled using Ahrefs, while AI citation trends were tracked using Ahrefs Brand Radar across multiple large language model platforms.
Although the sample size was limited, the sites were selected specifically because they appeared to be affected by the same algorithmic demotion, allowing for clearer comparisons. The result was a consistent pattern across every dataset examined.
Organic Visibility Losses Were Matched by AI Citation Declines
All 11 subfolders in the study lost Google organic traffic. Every one of them also lost AI search citations.
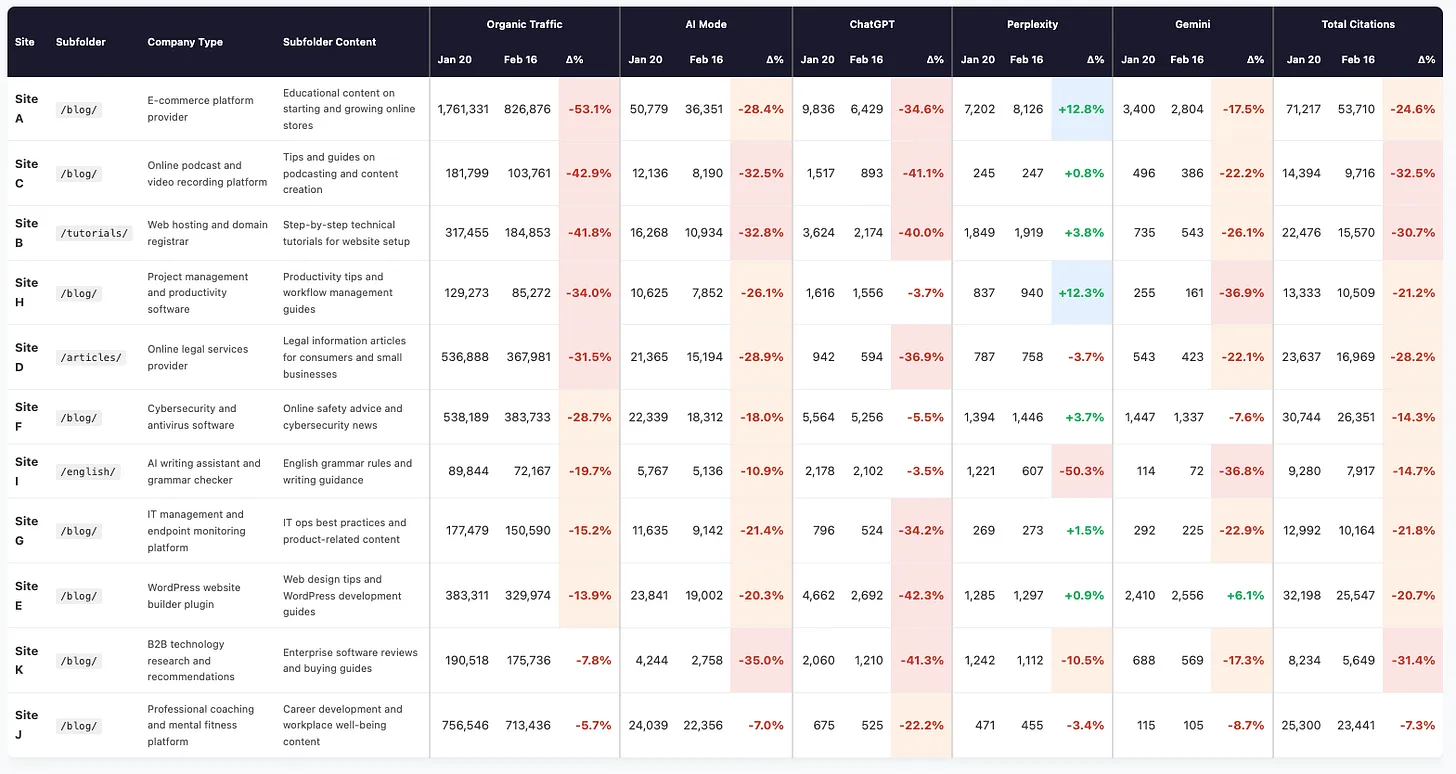
On average, organic traffic dropped by 26.7%. Over the same period, total AI citations declined by 22.5%. The platforms most closely aligned with Google’s search results showed the strongest correlation.
Google AI Mode recorded an average citation decline of 23.8%.
ChatGPT followed closely with an average decline of 27.8%, in several cases exceeding the scale of the organic traffic losses. Gemini reflected similar trends, though with more moderate reductions.
Ray noted that the consistency of the declines suggests AI systems are not relying on static knowledge alone. Instead, they appear to be influenced by the same ranking signals that shape Google’s search results.
ChatGPT’s Dependence on Google Appears Stronger Than Expected
One of the most revealing findings involves ChatGPT.
Despite being a non-Google product, ChatGPT showed the steepest citation losses across nearly every affected subfolder.
Five of the 11 sites experienced citation declines exceeding 34% on ChatGPT, with one reaching over 42%.
This behavior suggests that ChatGPT’s web retrieval process may rely heavily on Google’s search results during live queries.
While no official confirmation exists, the data indicates that changes in Google rankings can have an immediate effect on what ChatGPT chooses to cite.
Notably, ChatGPT appeared more sensitive to these ranking shifts than Gemini, Google’s own conversational AI. Ray suggested this could mean Gemini draws from a broader or partially cached knowledge base, while ChatGPT may depend more directly on live search signals.
Perplexity Followed a Different Pattern
Perplexity stood apart from the other platforms.
Only four of the 11 subfolders saw citation declines, and the average change was a modest 2.9% decrease. Seven subfolders actually gained citations despite losing organic traffic on Google.
This divergence aligns with existing evidence that Perplexity relies primarily on non-Google search sources, including the Brave Search API and its own crawler. Even when Perplexity citations declined, the changes did not correspond to the severity of Google ranking losses.
However, Ray cautioned that relative independence does not equal equal impact. ChatGPT’s scale remains far larger.
Citing Similarweb data, the study notes that ChatGPT received 5.8 billion web visits in August 2025, compared to 148.2 million for Perplexity.
Why This Matters for SEO and AI Strategy
The study reinforces a growing reality for publishers and brands: AI visibility cannot be separated from search performance.
Ray cautioned against tactics designed solely to increase AI mentions at the expense of organic rankings, including cloaking, hidden prompt injections, or overly promotional content formats.
While such approaches may produce short-term gains, the data suggests they can result in lasting visibility losses across both search engines and AI platforms.
“If you drop in organic search,” Ray wrote, “you can likely expect a corresponding drop in citations not only from Google’s own AI search products, but from other LLMs like ChatGPT as well.”
What This Means for Publishers and Brands
The research challenges the idea that AI search represents a separate recovery channel for sites that lose Google visibility.
The data shows there is no independent path to sustained AI exposure that bypasses search performance. Sites that lost ground in Google not only saw fewer clicks but also appeared less frequently as cited sources in AI-generated answers.
In practical terms, AI-driven search increases the cost of ranking declines. A drop in Google visibility now impacts multiple discovery channels simultaneously.
The Bigger Picture
Strong organic rankings continue to influence how AI systems select and surface sources. When search visibility declines, AI citations often follow.
ChatGPT appears particularly responsive to changes in Google rankings, even more so than some Google-owned AI tools. Perplexity operates with greater independence but at a significantly smaller scale.
SEO fundamentals remain the primary driver of discoverability across both traditional search and AI-generated results.
Key Takeaways
- Every site studied lost AI citations after Google ranking declines.
- Average AI citation losses reached 22.5%.
- ChatGPT showed the strongest correlation with Google visibility.
- Gemini followed similar trends with smaller declines.
- Perplexity showed relative independence but limited scale.
Zulekha
AuthorZulekha is an emerging leader in the content marketing industry from India. She began her career in 2019 as a freelancer and, with over five years of experience, has made a significant impact in content writing. Recognized for her innovative approaches, deep knowledge of SEO, and exceptional storytelling skills, she continues to set new standards in the field. Her keen interest in news and current events, which started during an internship with The New Indian Express, further enriches her content. As an author and continuous learner, she has transformed numerous websites and digital marketing companies with customized content writing and marketing strategies.