Table of Contents


Want to Boost Rankings?
Get a proposal along with expert advice and insights on the right SEO strategy to grow your business!
Get StartedWhen Google rolled out its “before:” and “after:” search operators in 2019, many SEO professionals and researchers were excited by the potential to filter search results based on specific dates.
These operators allowed users to narrow down search results to a specific time frame, which enabled more relevant search results. However, despite being introduced six years ago, the “before:” and “after:” operators are still in beta.
Free SEO Audit: Uncover Hidden SEO Opportunities Before Your Competitors Do
Gain early access to a tailored SEO audit that reveals untapped SEO opportunities and gaps in your website.

While some may have forgotten about them, the “before:” and “after:” operators still hold significant value for power users, especially for marketers, content strategists and researchers.
Till now, there is no clear timeline for their full rollout. It is a surprising fact that has left many wondering about the delay and the reasons behind it.
Six years later, Google’s search operators for before: and after: are still in beta https://t.co/oHNRvonbqy pic.twitter.com/gYR7QkNx8w
— Barry Schwartz (@rustybrick) May 6, 2025
The Power of the “Before” and “After” Operators: How They Work
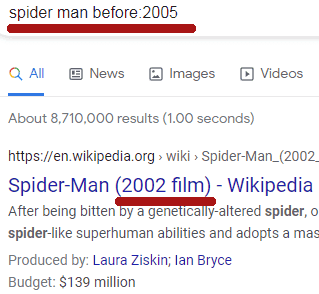
The “before:” and “after:” search operators allow users to filter results by specific dates or date ranges. For example, a search like:
- avengers endgame before:2019
Would only bring up results that were posted before 2019, while:
- avengers endgame after:2019-04-01
Would show results published after April 1, 2019. You can also combine both filters, such as:
- avengers endgame after:2019-03-01 before:2019-03-05
This search would yield results for Avengers: Endgame content published between March 1 and March 5, 2019. This type of flexibility in narrowing down search results based on dates. But here is the catch that these are still in Beta even after the official announcement.
Danny Sullivan’s Revelation on Bluesky
Danny Sullivan, Google’s Search Liaison, recently drew attention to the topic with a response to a user’s post on Bluesky.
“We have before: and after: operators that are still in beta.”
He continued to explain the functionality of these operators, which many users have been familiar with since their release, adding:
“You must provide year-month-day dates or only a year. You can combine both. But the tricky part is determining the exact date of a document. There is no standard way that all site owners use to indicate a publishing or republishing date.”
Sullivan’s statement focuses on the critical issue that while the operators are useful, Google still faces challenges in accurately determining the exact dates of content due to inconsistent practices across websites. Some websites do not provide publication dates at all and many don’t distinguish between original publication and republishing or updating content.

This issue leads to a lack of accuracy when applying date filters to search queries.
Why Does Google Have Trouble Determining Publication Dates?
The issue Danny Sullivan highlighted is not new. Google’s search engine has long had difficulty determining the publication dates of content. Some of the reasons for this include:
- Many websites fail to use structured data to indicate the publication date, which makes it difficult for Google algorithm to extract this information.
- Even when websites do use dates, there is no universal format for indicating when content was first published or updated.
- Websites often update old content with fresh information, but may not alter the original publish date. This creates a situation where a search engine may mistake updated content for new content.

How “Before” and “After” Operators Still Offer Value
Despite the challenges, these operators are still quite useful for power users, especially those in research and marketing.
Marketers could use the operators to track content performance or see how a certain topic evolved over time. Researchers could use them to find studies or articles published in specific months or years, which provide a way to trace the development of scientific thought or industry trends.
For example, let’s take a look at a content marketer analyzing the release of Avengers: Endgame. By using the following search:
- avengers endgame after:2019-04-01 before:2019-05-01
The marketer can see how conversations about the movie developed in the first month after its release. This could inform future campaigns or help track audience engagement patterns.
| Did You Know!
A study conducted by Ahrefs on SEO trends found that content published within the last year is typically 1.5x more likely to rank higher in Google search results than older content. This highlights the importance of time-sensitive searches and filtering content by specific dates to monitor ranking trends. |
How to Maximize the Use of “Before” and “After” Operators
Despite their beta status, the “before:” and “after:” operators still offer valuable utility for users who know how to leverage them effectively. Here are some tips to make the most of these operators:
- Combine before: and after: with filters like site:, intitle:, or inurl: to refine searches. For example, site:techcrunch.com intitle:”AI” after:2023-01-01 before:2023-12-31 finds AI articles from 2023 on TechCrunch.
- Use these operators to track how topics grow over time. For example, “remote work” before:2020-03 vs. “remote work” after:2020-03 shows how the narrative changed during the pandemic.
- Identify industry trends with before: and after:. For example, intitle:”NFT” after:2021-01 before:2021-12 reveals how NFTs were covered during their rise.
While it may seem perplexing that Google’s “before” and “after” operators are still in beta after six years, it highlights the ongoing challenges Google faces in perfecting search. However, for those who understand these limitations and know how to use the tools effectively, they continue to be a powerful asset in refining search results.
About the author
Share this article
Find out WHAT stops Google from ranking your website
We’ll have our SEO specialists analyze your website—and tell you what could be slowing down your organic growth.