Do 404 Errors Matter in SEO? Best Practices and Google Insights
By: Ananyaa Venkat | Updated On: July 3, 2024
Table of Contents
404 errors may look pretty common yet frustrating for internet users. However, it is more daunting for SEOs and website owners.
In fact, this question- will 404 errors hurt SEO?- is repeatedly being asked somewhere or the other across the SEO community.
So, what’s all the noise around 404 errors? Are they a ranking signal and worth the hype? What does Google have to say about it all?
In this write-up, I will break down 404 errors in detail to help you get all of these questions regarding 404 errors answered.
Alright. Without any ado, let’s get started.
Want to see your website at the top? Don’t let your competitors outshine you. Take the first step towards dominating search rankings and watch your business grow. Get in touch with us now and let’s make your website a star!
Understanding 404 Errors
A 404 error page is what the user sees when they attempt to visit a page that doesn’t exist on a website. It’s the computer’s way of saying that the requested page is not found.
So, what happens behind the scenes?
Imagine going to a grocery store to buy some eggs for breakfast. You ask the storekeeper and he first checks for the availability of the item and lets you know the status. That’s exactly how it goes between the browser and the server.
When the user enters a URL on their web browser, the browser goes to the website’s server and asks, “Hey, can I get this particular web page?“
When a user request comes in to visit a specific page on a website, the server returns an HTTP status code in response. In most cases, the server returns a 200 response code, which indicates that the user can access the content. I mean, if you are reading this blog post, it is because our server returned a 200 HTTP response code.
But what if the server can’t find the page anywhere? That’s when the 500 series errors and 404 error occurs.
Google’s Stance on 404 Errors
Google has long maintained that having pages return a HTTP 404 status code is a normal part of web management. Most websites encounter these errors, and when a page does not exist on your site, a 404 status code is the proper response.
However, Gary Illyes from Google recently shared insights on LinkedIn, highlighting specific scenarios where webmasters should address and fix pages returning a 404 status code.
Illyes began his LinkedIn post with a familiar Google Search disclaimer: “404 (Not found) errors are not to be afraid of and you don’t need to scramble to fix them, at least not most of the time.” He then delved into situations where addressing 404 errors becomes necessary.
A 404 error is triggered when a URL on your server does not map to any existing resource. Illyes explained that these URLs fall into two main categories:
- The URL Should Return Content (200 Status Code): This situation arises when an important page is accidentally deleted or there is an issue with the database, leading to the absence of expected content. These errors should be fixed promptly, especially if the URL is crucial for users and the site’s functionality.
- The URL Should Not Return Content:
- URLs That Could Be Useful to Users: These URLs should be mapped to relevant content, possibly through redirects. For instance, broken links from high-traffic pages that could lead users to valuable content should be addressed.
- URLs That Are Absolutely Useless: These should remain as 404 errors. Fixing these might mislead users, such as off-site links to content that no longer exists because of a change in business focus.
Illyes highlighted the importance of understanding when to fix 404 errors, emphasizing user experience. If a URL is important and has user traffic, fixing it can significantly improve user satisfaction and site usability. Conversely, fixing URLs that are genuinely irrelevant can mislead users and waste resources.
Moving forward, the focus will be on strategic fixes that prioritize user-centric issues. This approach aligns with Google’s broader emphasis on enhancing user experience and ensuring content relevance. Webmasters are expected to adopt a more discerning approach, addressing only those 404 errors that have a significant impact on user satisfaction and site performance.
SEO Impact of 404 Errors
404 error pages are pretty common and it is one of the most frequently encountered HTTPS errors across the web. The existence of a few 404 pages doesn’t affect your site’s overall performance and rankings.
As Google says, “The fact that some URLs on your site no longer exist or return 404 errors does not affect how your site’s other URLs (the ones that return 200 (Success) status codes) perform in our search results.”
However, it can impact your rankings if found in abundance and if the pages that return with 404 are integral to your website. Here are a few such scenarios in which you have to fix 404 errors on priority.
404 Error Impact on Backlinks and Authority
Imagine your website once had a highly successful page focused on marketing strategies during COVID-19. This page garnered significant organic traffic and high-quality backlinks. But now, as life normalizes and the content becomes less relevant, you’re considering removing this outdated post. However, there’s a catch.
When you delete this page, all those valuable backlinks will lead to a 404 error page, which can erode the authority your website has built. This is where strategic thinking comes into play.
Instead of outright removing the page, consider two better options:
Keep the Page: Sometimes, it’s wise to keep the page live. Even if it’s not drawing the same traffic, it still holds SEO value due to its backlinks.
Use a 301 Redirect: More effectively, you can replace the old content with something current and pertinent. For instance, create a new page about adaptable marketing strategies for future uncertainties. Then, 301 redirect the old COVID-19-focused page to this new one. This way, Google recognizes that you’ve updated your content to stay relevant, and the authority from the old page transfers to the new one.
This approach ensures you retain the SEO benefits and adapt to changing times without losing your site’s established authority.
SEO Impact of 404 Pages after Hack or Malware Attack
Indeed, there are scenarios where 404 errors can actually benefit your website, rather than harm it. Consider a situation where your website suffers a malware attack, resulting in hundreds or thousands of pages being wrongly indexed on Google. These pages might contain harmful content for users.
After successfully removing the malware from your server, it’s likely that these maliciously added pages will start showing 404 errors. In this case, it’s crucial not to automatically redirect these 404 pages to your homepage. This is a common mistake among webmasters. Instead, it’s advisable to leave these corrupted pages as 404s. Over time, which varies depending on the number of pages indexed, Google will recognize these pages as non-existent and remove them from its index. Implement a 301 redirect only for those pages that have contextually relevant and similar content.
Tips: If you want to remove the hacked pages from appearing on Google search, use the Temporary Removal tool in the search console.
What this means is that 404 errors on a less important and low traffic driving page will not lead to a negative impact on your overall website’s rankings.
Impact of 404 Errors on Website Bounce Rates
404 errors significantly increase website bounce rates. Typically, when users encounter a 404 error page, they are unlikely to explore further, perceiving the website as unreliable. This not only elevates bounce rates but also damages the website’s reputation.
Moreover, Google now factors in user engagement as a key aspect of SEO rankings. If visitors quickly exit a page, Google interprets this as the content not meeting user expectations, potentially leading to the page’s diminished visibility in search results.
Furthermore, encountering multiple 404 errors within a site, especially through internal links, severely disrupts the user experience. This not only ends the user’s journey abruptly but also negatively impacts the website’s standing with Google. Consequently, pages linked to 404 errors are less likely to achieve high rankings in search results, as Google aims to ensure a seamless experience for its users.
Effects of 404 Errors on Googlebot’s Crawl Efficiency
Googlebot, Google’s web crawler, scans websites to discover new and updated pages for indexing. However, a website with numerous 404 error pages can exhaust its allocated crawl budget. This overuse of resources may result in significant pages being overlooked during crawling, delaying their indexing.
Common Causes of 404 Errors
So, what triggers 404 errors? Here’s a look at the most common causes.
Broken Links
Broken links are born when a page is not properly linked to the destination URL. Misspelled URLs are one of the most common reasons behind the existence of broken links. When this happens, the user doesn’t get redirected to the page you want them to land on. Instead, they find themselves on a 404 error page.
Deleted or Moved Pages
If you move your content to a new destination or delete it altogether but don’t remove the old URL from whichever pages you placed them, you are driving your users to a 404 error page.
URL Changes
URL changes can be another catalyst for the appearance of 404 pages. If you update your page URL but fail to change it in your content where you have placed links to that particular page, you drive users to a non-existent page and open doors to 404.
How to Identify 404 Errors on Your Website
To weed out 404 errors on your website, you need to know where they exist in the first place. Here’s a look at the ways you can execute it.
Google Search Console
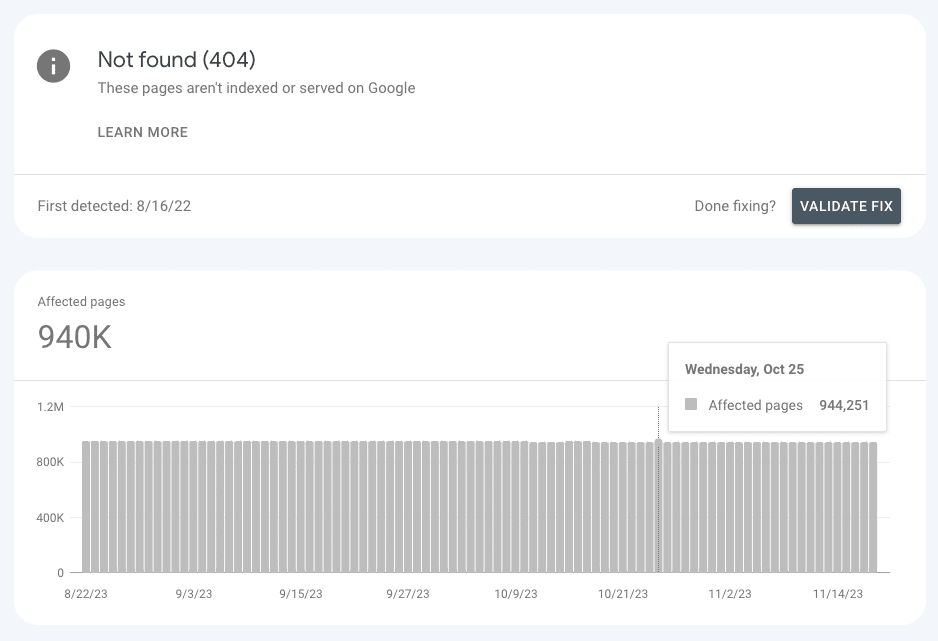
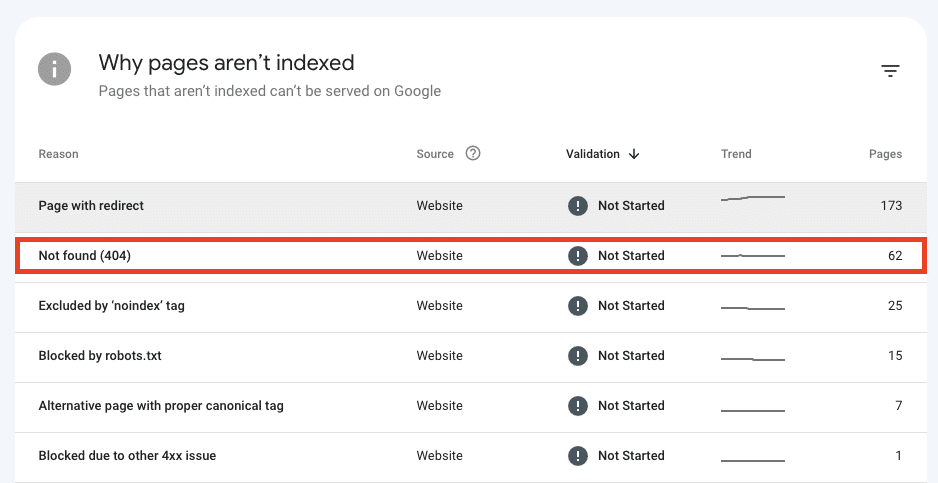
If Google finds 404 errors when crawling your site, it will notify the same via the Coverage Report in Google Search Console.
Similarly, once you fix the errors on your website, you can use the Validate Fix option in Google Search Console to bring it to Google’s notice in order to prompt the search engine to recrawl your site and evaluate the bug fixes you have made.
And that brings us to this question. What does Google do to validate fixed 404 errors? Nevertheless, it will still remain a 404 page. So, what actually happens behind the scenes?
Replying to a similar question on X, John Mueller, Senior Search Analyst / Search Relations team lead at Google, wrote, “It’s more if you accidentally 404’d something and fixed it. You obviously don’t have to fix 404s that you want to be 404s. Also, this is more about tracking for you (“I fixed this, tell me when you see it fixed too”).”

From what he says, validation of fixed 404 errors is more about keeping track of fixes for web pages that accidentally disappeared. After all, you don’t have to do anything about pages you intentionally don’t want to exist, right?
In other words, the 404 status code is not necessarily a bug that a webmaster has to fix. It is just that Google leverages the Validate Fix feature to keep an eye on missing pages in order to show them in SERPs once or if they return.
Semrush
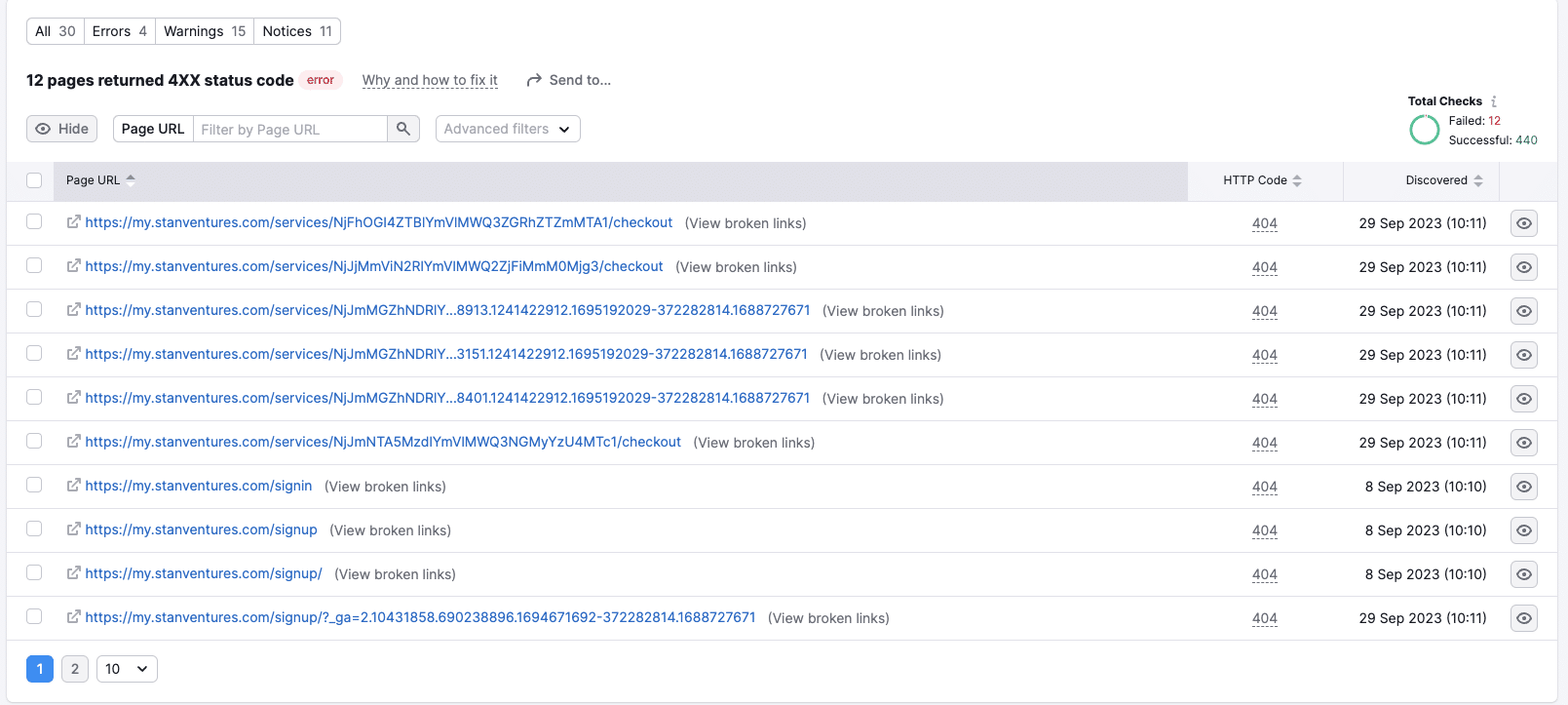
The Semrush Site Audit tool comes in handy to crawl your website and identify potential on-page and technical issues lurking on your site. Using this tool is a good way to identify 404 errors on your website.
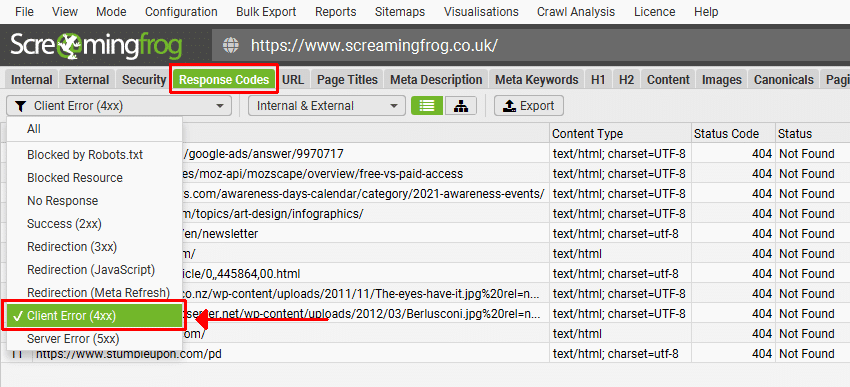
Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is another great tool to audit your site and locate on-page issues easily. Once the tool finishes crawling your site, navigate to Client Error (4xx) under Response Codes in the drop-down menu. That should help you narrow down 404 errors on your website.
Manual Checks
Checking your web pages manually for 404 errors may be time-consuming. However, it is a good way to double-check and fix 404 errors and other potential problems on your website.
How to Fix 404 Errors
Now that you know how to identify 404 errors on your website, let’s get to how to fix them.
Setting Up 301 Redirects
301 redirects allow users to automatically redirect to the new destination when they are about to land on a page that doesn’t exist anymore. This way, you stop your visitors from hitting a 404 dead end.
So, how do you do it?
- Install a trusted free redirection plugin for WordPress
- On WordPress, go to Settings and navigate to the 404 tab
- Check for issues and, in the Redirect section, enter the URLs from which you want to redirect users
- Enter the new URLs in the Destination tab and save the changes
Updating Internal and External Links
Check your internal links carefully and identify the ones that lead to 404 pages. Replace them with new URLs to make sure your visitors are taken to the right pages on your website. This paves the way for improved user experience within your website.
On the other hand, updating external links that bring users from another site to a 404 page on your site takes a bit more work. Unlike internal pages that are completely in your control, your external links are placed on sites that are owned by others.
To fix such incoming 404 errors, you have to get in touch with corresponding webmasters with a genuine email pitch to replace your old URL with the new one or a link removal request in case of deleted pages that don’t have an alternative.
Creating an Effective Custom 404 Page
Rectifying 404 errors strengthens your website’s SEO. However, it is not always possible to eliminate 404 errors because certain factors, like a user typing a misspelled URL, are out of your control. That’s why it is essential to create a custom 404 page for your website.
You can do this by using a free plugin for custom 404 page creation. In your custom 404 page, you can include elements like a search box, links to important pages on your website and your contact information.
Such a 404 page is user-friendly because it provides visitors with potential options to search for and explore relevant sources and interact with your website.
Monitoring 404 Error Pages
It is good to monitor your site from time to time for potential 404 errors, especially when you update parts of your website or revamp it entirely.
As I mentioned earlier, you can use tools like Google Search Console, Semrush Site Audit Tool, Screaming Frog and more to identify and fix 404 errors.
By monitoring your site from time to time, you can take steps to fix visible 404 errors at the earliest, even if not root them out completely.
What is the Difference Between Hard 404 and Soft 404?
Want to delve deep into 404 errors? Here comes Hard 404 Vs. Soft 404.
Hard 404 is the usual 404 error we’ve discussed above. If the page doesn’t exist, the server returns a 404 error code.
On the flip side, soft 404 error pages return a 200 OK status code, which means it is alright for the search engine to crawl those web pages.
In fact, Gary Illyes’ latest LinkedIn post confirms the same and gives more insights into why soft 404 errors are bad for SEO.
Illyes explains, “crawlers use the status codes to interpret whether a fetch was successful, even if the contents of the page is basically just an error message. They might happily go back to the same page again and again wasting your resources”.
Now, this crawl behavior of Google spiders based on the 200 OK status code will be a waste of the crawl budget Google has allocated for your site. After all, these error pages hardly contain any valuable content.
As a result, soft 404 pages may exhaust your crawl budget and prevent Google from crawling your important pages. However, they just don’t stop there.
Again, as Illyes wrote, “Crawlers have lots of resources, they can afford to waste some, your site likely doesn’t. Soft errors are bad because:
- The limited “crawl budget” spent on them could’ve been spent on real pages.
- the pages will unlikely to show up in search because during indexing they’re filtered out, basically no ROI on the resources you’ve spent on serving them.”
That said, apart from getting your crawl budget wasted on useless resources, soft 404 error pages are filtered out during the indexing process so that they may not appear in search results.
That means you don’t get any substantial benefit for your website, such as traffic, rankings or online visibility, out of the time and effort you put into those pages.
Also, as the pages don’t return a 404 error code, it is pretty difficult to detect these pages using SEO tools.
Given the scenario, soft 404 pages can be a threat to your website’s health and SEO, especially if you don’t handle them the right way.
A Case Study of Fixing 404 Errors
Concern:
Gourmet Delight , an online recipe sharing platform, noticed a gradual decline in website traffic and user engagement over six months.
Problem Identification:
An SEO audit revealed a significant number of 404 errors. These were mostly due to deleted seasonal recipe pages and altered URLs during a recent site redesign.
Strategy
- Redirecting Valuable Pages: For deleted recipes that had high backlinks and traffic, the team set up 301 redirects to relevant seasonal recipe collections.
- Fixing Internal Links: They updated all internal links that led to 404 pages, ensuring users were directed to existing content.
- Custom 404 Page: A custom 404 page was created, featuring a search bar, popular recipe categories, and a friendly message to guide lost users.
Results
- Improved User Experience: The bounce rate decreased by 30% within three months.
- Recovered Traffic: Redirected pages saw a 25% increase in traffic, as users were guided to relevant content.
- SEO Ranking: Within four months, the site regained its previous Google ranking position, and user engagement metrics improved.
By strategically addressing 404 errors, GourmetDelight.com enhanced user experience and SEO, demonstrating the importance of regular website audits and responsive SEO practices.
404 errors are quite common. However, if you let them spread across your website, they are strong enough to affect your user experience and even bring down your domain authority and Google rankings in the long run. That means, if ignored, 404 errors can harm your website’s SEO seriously.
Put the methods I have suggested above into practice in order to identify and fix 404 errors as much as possible. Make sure you follow the best practices and monitor your site for 404 errors to offer a great user experience to your visitors and take another step towards securing a stronger spot in the good books of Google.
404 Error: Frequently Asked Questions
- How Long Does Google Take to Deindex 404 Pages?
It usually takes anywhere from a few days to weeks for Google to deindex a 404 page. However, the time frame also depends on other factors, such as the crawl rate of your website and how frequently the 404 page in question was updated in the past.
- Can I Personalize How Google Handles My 404 Error Pages?
No. It is not possible to customize the way Google handles your 404 error pages. However, following the best practices discussed above helps you to create a user-friendly 404 page and efficiently address issues related to 404 errors on your website.
- Should I redirect all 404 Errors to My Homepage?
Redirecting all 404 errors to your homepage can confuse your visitors and lead to a bad user experience. Instead, setting up 301 redirects to direct users to a new page that answers their queries and fixing broken backlinks are the best practices.
Get Your Free SEO Audit Now!
Enter your email below, and we'll send you a comprehensive SEO report detailing how you can improve your site's visibility and ranking.

You May Also Like
How to Harness First Contentful Paint (FCP) for Faster Page Loading
Did you know that improving site speed by just 1 second can bring 27% more conversions? Every user experience metric that takes you closer to that one–second improvement matters. There’s one metric that can help you showcase an excellent site speed and attract your visitors at the first instance. That is First Contentful Paint (FCP). … How to Harness First Contentful Paint (FCP) for Faster Page Loading
How to Leverage Time To First Byte to Boost Your Page Loading Speed
Do you still find your web page loading sluggishly even after optimizing its page speed? You are probably focusing on the front-end performance of your website. I suggest you pay attention to the backend as well. That’s where page loading begins. A slow Time To First Byte is one such server-side issue that is most … How to Leverage Time To First Byte to Boost Your Page Loading Speed
Decoding 500 Series Status Code Errors and SEO Impact
Explore the crucial implications of 500 Series server errors on SEO performance. Learn how to identify, diagnose, and resolve these critical issues.








Comments