SEO-Friendly URL Structure: A Definitive Guide for 2024
By: Ananyaa Venkat | Updated On: July 9, 2024
Table of Contents
When was the last time you took a closer look at your URLs?
Well, not many people optimizing their websites for search engines focus on the URL structure.
So, do you really have to care about your URL structure?
Yes, because, for Google, the URL structure matters.
That’s why here I am to tell you how the search engine looks at URL structure and how you can craft an SEO-friendly URL structure.
Let’s get started.
What is a URL?
A Uniform Resource Locator, known as URL in short, is the address you enter on the web to access a particular page.
URLs are links that people click on to visit web pages directly from Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Something like this.
What is URL Structure?
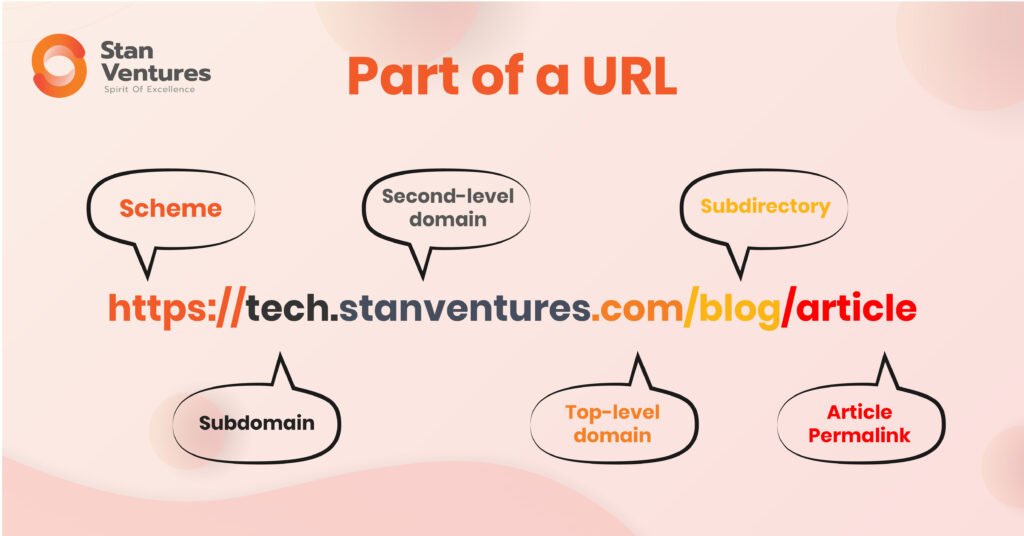
A URL is a combination of the following elements.
Protocol – Protocol denotes how the browser gets access to the information on a web page. It is usually http:// or https://.
Root Domain – This is the main name that’s unique to your website.
Subdomain– A subdomain separates a section of your site from the root domain in order to organize your content. The most commonly used subdomain is www.
TLD– Top-level domain (TLD) is what follows the root domain. It can be .com, .net, .org etc.
Slug – This is the category under which you place a particular web page.
Article Permalink– Following the slug, the permalink tells you what the page is about.
That’s how URL structure goes.
How Search Engines Use URLs
The ultimate goal of search engines is to fetch users the best results related to their search queries.
But how do they know what is relevant and what is not?
Search engines like Google empower their systems with advanced algorithms to fetch results. In fact, Google uses 200+ ranking factors to determine the relevance of content across the web to a particular user query.
Based on the relevancy signals that websites pass on to Google on the grounds of these ranking factors, Google evaluates the relevancy of web pages to a specific query.
So, let’s get to what brings us here; the URL.
Google looks at URLs as one such factor that sends relevancy signals to it.
Why URL Structure Matters for SEO
URLs can complement your SEO efforts in three ways, especially if they are crafted well. Check out the benefits below.
Better User Experience

A good URL hints to the users beforehand what the destination page contains. This way, the users get to know what they can expect to see on your page and how relevant it is to the search query they made.
From that standpoint, URLs can ensure an improved user experience.
After all, user experience relies heavily on whether the user finds what they are looking for on the target page.
The URL structure does serve this purpose well and opens doors to a great user experience when landing on your site.
Higher Rankings
As I said earlier, URL is a minor Google ranking factor. No matter small or big, every ranking factor counts, right?
So, don’t miss out on the ranking advantage your URL structure has to offer.
Search engines use URLs to determine the relevancy of pages to user queries. That’s why it is essential to make sure that your page URLs are relevant to your content.
While URLs are a minor influence on ranking, including keywords in your URLs can improve your chances of achieving higher rankings considerably.
Backlinks
A simple and comprehensive URL can sometimes create opportunities for you to place it directly in the content without embedding it in the anchor text.
An URL placed in such a way on an external site earns you a backlink. Backlinks are, of course, a top Google ranking factor.
Besides, you can use a naked URL to promote your content on social media. You don’t have to embed it in the anchor text.
Does the URL Structure Impact Google Rankings?
URL is a minor Google ranking factor. So, there’s no wonder that your URL structure impacts your search engine rankings.
SEO-friendly URLs promote your PageRank. PageRank is Google’s way of determining the relevance of web pages to search queries. The more the relevance, the higher the PageRank.
That’s reason enough why you need to focus on creating a URL structure that is search engine-friendly.
Besides boosting your PageRank, well-optimized URLs improve the chances of attracting more clicks when your page appears on search results. This way, your site will gain more organic traffic.
How Important are Keywords in URLs
Over the years, Google representatives have claimed that the inclusion of keywords in the URL can bring very little SEO benefit.
But here’s the thing.
Time and again, keywords give users and search engines a better context about the content.
That is what ultimately matters because Google constantly aims at fetching pages that are useful for users.
The clearer the context is for Google and the user, the higher your chances of showing up for relevant searches online.
This will drive more qualified leads your way and boost your conversion rate incredibly.
If that’s the result you aim for (naturally for any website owner), keyword placement in URLs is NOT something you will ignore.
Best Practices for Creating an SEO-Friendly URL Structure
Use HTTPS
The HTTPS protocol tells the search engine and your users that your website is secure. It signifies that you have a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) in place to encrypt the communication between your website and the browser.
This reduces the chances of your website being hacked and even if it is hijacked, the attackers won’t be able to access your data.
With the HTTPS protocol, you make your visitors feel more secure, especially when they enter their credit card information to buy your products or services.
That said, it passes trust signals to the search engine, which in turn, boosts your site’s credibility.
Avoid the WWW prefix
Any subdomain, including www, is used to organize a website’s content in a better way. In fact, the www prefix often gets hidden when your site appears on the browser.
So, why do you have to use it when you can conveniently categorize your content without it?
I’m not suggesting that adding subdomains is bad. But add one only when it is absolutely necessary.
For example, when you choose to have an URL structure like blog.example.com/ instead of example.com/blog, a subdomain becomes a necessity.
Use the Right TLD
If you want to magnetize web traffic on a global scale, I suggest you choose a generic top-level domain like .com
On the other hand, if you are targeting potential customers based on location, it’s best to opt for a location-specific TLD like .uk, .au, .in and more.
Make sure you avoid random TLDs like .name, .biz, .info and others.
Such TLDs are often associated with spam sites. So, stay away from them to protect the credibility of your site.
Keep it Short and Simple
The shorter the URLs, the easier it is for the search engines and users to make sense of your web page.
The better the search engine comprehends your page, the more the chances of your page ranking higher on SERPs.
So, ensure you avoid unnecessary string characters in your URLs and keep them as crisp and simple as possible.
Make it Descriptive
Your URL should serve a specific purpose.
What I mean to say is that the URL has to convey to the users what the page is about at the very first instance. It shouldn’t be confusing or misleading.
Remember that your URL is the capsule within which your content exists. That’s why it is important to keep it descriptive.
Include Appropriate Keywords
Keywords are a must-have to improve your search engine visibility. How about using them to bolster your URL structure?
Yes. Including keywords in your URL is a good way to send relevancy signals to the search engine and make your page quickly discoverable online.
BEWARE. Don’t stuff keywords in your URLs. That will bring a negative SEO impact on your site.
Make it a point to include just one or two relevant keywords in your URLs to make them SEO-friendly.
Categorize Your Pages Using the Right Keywords in the URL
Are you choosing a keyword to categorize your pages based on the search volume? You may be wrong.
Keyword search volume may be a top priority for other SEO strategies, but not when you use keywords in your URLs to categorize your pages.
Instead, choose keywords that closely describe what the pages in a particular category are about.
Separate words using hyphens
URLs don’t include spaces. Instead, they leverage hyphens.
Add hyphens to your URLs in places where a space is needed and NOT underscores.
Let me give you an example.
https://www.stanventures.com/blog/link-building/
Here, link and building are two separate words. Jamming them together with no break will make it difficult to comprehend.
So, there comes a hyphen.
In a nutshell, hyphens make your URLs easily readable for search engines and users alike.
Avoid Stop Words
URLs don’t require stop words, such as the, and, or, of, a, an, to, for, etc., to convey meaning. They are perfectly fine without them.
In fact, adding stop words only make your URLs complex and unnecessarily long.
So, eliminate stop words in your URLs to maintain SEO friendliness.
Use Lowercase Letters
URLs are case sensitive.
That’s why when it comes to URLs, it is recommended that you always use lowercase letters.
But why?
When you use characters other than lowercase letters in your URLs, they may take users to a 404 error page. That means your page can’t be found.
And the result?
You will lose your potential customers. That’s absolutely the last thing any website owner wants.
So, make sure you always opt for lowercase letters to craft your URLs.
Redirect Your Old URLs Properly
There are times when webmasters move the content to a different page or to a different domain altogether.
But what happens to the old page?
It shows a 404 error code when someone visits it and the user ends up finding nothing relevant to their search on your page.
That’s a negative SEO signal as it leads to poor user experience.
So, whenever you switch your content to a new page, make sure you leverage 301 redirects to rightly redirect users and search engine bots to your new page.
Avoid Using Dates
Let’s say you are publishing a new blog post on your site.
Now, if you are including the date of publication in your URL, you are committing a big mistake.
Why?
The inclusion of dates in your URL will make your content outdated with time.
Suppose your blog is published in 2022. For someone visiting the page in 2025, the occurrence of the date of publication in the URL will suggest that your content is out of date.
That said, never include dates in your URL.
Eliminate Numbers
Including numbers will make your URL look quite long. As you know, the shorter the URL, the better it is for SEO.
So, don’t use numbers in URLs unless it is absolutely necessary to convey meaning.
For example, yoursite.com/blog/seo-basics-234567/ is a bad URL, while yoursite.com/blog/5-types-negative-seo/ is a good one.
Avoid Dynamic URLs
Users are the primary focus of search engines. So, search engine bots don’t particularly like anything that directly or indirectly hinders a smooth user experience.
From that standpoint, dynamic URLs aren’t SEO-friendly.
Why?
Dynamic URLs, such as the ones with UTM tracking, are quite complex and difficult for users to understand.
So, when you focus on creating SEO-friendly URLs, make sure you don’t opt for dynamic URLs.
Facilitate Easy Navigation
Not all users land on your homepage. Some land on a blog post, while some others land on a service page.
Alert: hassle-free navigation within your site is another sign of a good user experience.
So, how do users find where exactly they are on your page?
It’s possible with a well-crafted URL structure.
Create your URLs in such a way that the users know where they are on your site at a given point of time.
Suppose a user lands on the below page of the Stan Ventures blog directly from Google search.
https://www.stanventures.com/blog/mobile-first-indexing/
From the URL, they will instantly know that they’ve landed on the Mobile-First Indexing page under the blog section.
Plus, they can easily navigate to our blog content repository or our homepage easily. That’s the power of a good URL.
Google’s Guidelines for Crafting an Optimal URL Structure
Google’s recommendations for URL structure are clear and straightforward. They advocate for the use of simple, descriptive words in URLs, localized words if applicable, and UTF-8 encoding for non-ASCII characters.
However, Google advises against using non-ASCII characters directly in the URL and using long, unreadable ID numbers.
Let’s delve deeper into these guidelines to understand how to create a URL structure that Google loves.
Google Recommended Practices
| Practice | Example |
|---|---|
| Simple, descriptive words in the URL | https://www.site.com/blog/seo-tips |
| Localized words in the URL, if applicable | https://www.site.com/food/mint |
| Use UTF-8 encoding as necessary for non-ASCII characters | https://www.site.com/%D9%86%D8%B9%D9%86%D8%A7%D8%B9 |
| UTF-8 encoding for emojis in the URL | https://site.com/%F0%9F%A6%99%E2%9C%A8 |
| Country-specific domain for multi-regional sites | https://site.fr |
| Country-specific subdirectory with gTLD for multi-regional sites | https://site.com/fr/ |
| Using hyphens (-) to separate words in URLs | https://www.site.com/summer-clothing |
Google Not Recommended Practices
| Practice | Example |
|---|---|
| Unreadable, long ID numbers in the URL | https://www.site.com/index.php?id_sezione=360 |
| Using non-ASCII characters in the URL | https://www.site.com/منتجات |
| Words in the URL joined together | https://www.site.com/bluedress |
| Using underscores (_) in URLs | https://www.site.com/summer_clothing |
| Using URL fragments to change content | https://www.site.com/#/productshttps://www.site.com/#/services
|
Many people underestimate the SEO capabilities of URL structure. The truth is when used right, URLs can bring several benefits, from increased organic traffic to higher rankings, to your website.
Implement the URL structure best practices that suit your site and let us know what worked for you in the comment section.
URL Best Practices Recommended by Google Executives
Category Structure – Hierarchical vs. Flat
For larger websites Gary Illyes is an Analyst on the Google Search team recommends a hierarchical category structure. According to him, this structure provides a clear, logical pathway for users to navigate and for search engines to crawl the site. It allows for efficient organization of content into broader categories and subcategories, facilitating better user experience and search engine optimization.
In contrast he suggest flat structure for smaller sites where a hierarchical system might be overcomplicated. The simpler structure of a flat system ensures that all pages are only a few clicks away from the homepage.
Language in URL Slugs – English vs. Other Languages
According to Garry, the choice between using English or the other language in URL slugs depends on the target audience and content strategy.
Using the other languages in the URL can be advantageous for local SEO and for users who search in that language. It can improve the relevancy of the URL to the content and enhance user experience for a specific audience.
However, he recommends using English in URLs if the focus of the website is global global audience or primarily English-speaking. It can make URLs more accessible and understandable to a wider audience.
Impact of Double Slashes in URLs:
Using double slashes in URLs (like https://example.com//page) is generally not a significant SEO issue. However, Garry says it’s important to maintain consistency in URL structures for better usability and clarity.
Double slashes can cause confusion for both users and crawlers. It might give the impression of a mistake or oversight in the URL structure, potentially affecting the user’s perception of the site’s professionalism.
Consistent, clean, and well-structured URLs are important for usability and can indirectly influence SEO through better user engagement and clearer site architecture.
Types of URLs – Absolute URL and Relative URL
As a website owner, you may have to use your URLs differently for different purposes. There are two types of URL formats that you would be predominantly using – Absolute URL and Relative URL.
What is Absolute URL?
As the name suggests, absolute URL is the complete URL of your website, which includes the HTTP protocols, non www or www version, the main domain, and the path to the subfolders. An Absolute URL provides the users and search engines with 100% information required for it to land on a specific page on your website.
Here is an example of absolute URL:
https://www.example.com/subfolder/page.html
In this example:
- “https://” represents the HTTP protocol used for secure communication.
- “www” is the subdomain (optional). It can be omitted if not used.
- “example.com” is the main domain name.
- “/subfolder” represents a subfolder within the website’s directory structure.
- “/page.html” is the specific page within the subfolder.
What is a Relative URL?
A Relative URL will only showcase a fraction of what you would see inside an absolute URL. Basically, it will omit the HTTP protocols, non www or www versions, and the main domain. Instead, it will only display the subfolders that lead to the specific URL.
Here is an example of relative URL: /subfolder/page.html
- “/subfolder” represents a subfolder within the website’s directory structure.
- “/page.html” is the specific page within the subfolder.
The relative URLs are used mostly by developers and webmasters to link from one page to another within the same domain. Most CMS platforms can understand this and the system can automatically assign the other URL properties that have been excluded.
When to use Absolute URLs?
It’s important to use absolute URLs in a few scenarios or it may lead to indexing, crawling and ranking issues.
XML Sitemaps
Imagine you’re creating an XML sitemap to guide search engine bots to discover all the pages on your website. In this case, you should use absolute URLs. Major search engines like Google and Bing require these absolute URLs in their guidelines to ensure there’s no confusion about which pages to explore.
Hreflang attribute
Suppose you have a website that publishes content in multiple languages. You want to make it clear that all these versions are just the translated versions of the same page and not unique pages. That’s what a hreflang URL does for your web pages. Adding the hreflang attribute will help prevent confusion. However, you should use absolute URLs for hreflang tags or the search engines may fail to identify the preferred version of the page.
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en” href=”https://www.example.com/page.html”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”fr” href=”https://www.example.com/fr/page.html”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”de” href=”https://www.example.com/de/page.html”>
In this example, each language version of the page has its own unique URL. By specifying the hreflang URL for each language version, you are indicating to search engines that the corresponding URL is the preferred version for that specific language.
This helps prevent confusion and ensures that search engines understand the relationship between the different language versions of the page.
Canonical URLs
Suppose you have two similar pages that are being indexed and ranked by Google. In a way, your organic traffic is getting diluted and there is a probability that Google isn’t ranking you higher because it’s confused about which page to rank for. In such circumstances, you can tell Google which page is your preferred or canonical version. This means that even though the pages have similar content, they are not considered duplicate or separate pages.
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/page1.html“>
In such cases, you cannot use a relative URL as Google and other search engines have asked only to use absolute URLs or the canonicalization remains null.
Ensure that you use absolute URLs in the canonical tags to provide the full URL for each page. Adjust the href attribute to match the respective URL of each page accordingly.
When to use Relative URLs?
There are multiple instances wherein you may have to use relative URLs. However, this is usually in the backend of your website or during the design and development phases.
Development Phase
It’s recommended to use the relative URLs while the website is in the development stage as the website is usually hosted in a staging server. If you use the absolute URL of a staging server for the links, you may end up having to change the links later after moving to the live server. To avoid such pitfalls, it’s ideal to use a relative URL.
Here is an example of a staging URL:
https://staging.example.com/blog/blog1/
Third-Party Plugins
There are a few third-party plugins that require you to only use the relative URL. One such example is OptinMonster. When using this plugin, you only need to enter the relative URL to trigger pop-ups. If you try adding an absolute URL, the system will automatically omit and use only the relative URL.
There are a few 301 redirect plugins that also require only the relative URL instead of absolute. However, these plugins are integrated into the website directly which is why they find adding absolute URLs a redundant process.
Get Your Free SEO Audit Now!
Enter your email below, and we'll send you a comprehensive SEO report detailing how you can improve your site's visibility and ranking.

You May Also Like
Turnaround Time (TAT) for SEO Projects: How Agencies Set Expectations
As an agency owner, the key to delivering a faster ROI for your clients is promptly implementing the proper SEO strategies. However, managing hundreds of client websites simultaneously means each client expects rapid results. That’s why your SEO agency must set clear expectations about turnaround time (TAT) with your clients, ensuring they understand the process … Turnaround Time (TAT) for SEO Projects: How Agencies Set Expectations
6 SEO Pricing Models for Agency Owners
When it comes to SEO service pricing, it can be difficult to know what is a fair price and what is too much. Read this blog to know more.
What’s a Good Click-through Rate?
Checkout some of the most effective ways to improve the CTR (Click Through Rate) which is one of the hidden search engine ranking factors.









Comments