Google Ranking Factors – 200+ Confirmed and Retired Signals
By: Ananyaa Venkat | Updated On: December 27, 2023
Table of Contents
As you may know, there are over 200 factors influencing Google algorithms.
To rank higher on SERPs, it is SUPER important to know which of these factors are proven and pivotal to follow and which ones are controversial and rooted in SEO speculation.
So, let’s delve into the complete list of 200+ Google ranking factors in 2024 straightaway.
10 New Ranking Factors Revealed from the Exhibits Submitted as Part of the Anti-Trust Case Against Google
The recent antitrust case against Google has opened up a Pandora’s box of new revelations. Thanks to a series of exhibits that have been produced before the justice department, we now have a few more signals that Google’s algorithms are using to rank websites on the search results pages.
These revelations provide a deeper understanding of what drives search rankings, underscoring the ever-evolving landscape of Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
Here are some of the newly disclosed Google ranking factors. These new signals should offer you a fresh perspective on how to optimize your SEO strategies moving forward.
1. Three Pillars of Ranking: Body, Anchors, and User Interactions
Google has emphasized three core elements in ranking: the body (content quality), anchors (backlinks), and for the first time user interactions (engagement metrics). This focus highlights the need for well-crafted content, strong backlink profiles, and engaging user experiences to improve search rankings.
2. Significance of User Data and Interactions
Google’s algorithms are increasingly considering user behaviors, such as clicks (whih they have been denying for a long time), attention on search results, and query reformulations. These user interactions are now crucial indicators of a page’s relevance and usefulness, playing a pivotal role in its ranking.
3. Data-Driven Insights: The Role of Logging and Analysis
The collection and analysis of user data have become integral ranking factors. This data-driven approach helps Google in understanding user preferences through their behaviors, enabling more targeted and effective results.
4. Importance of Understanding Real-World Queries
Google’s enhanced ability to interpret real-world, situational queries underscores the significance of content context and user intent. Optimizing content to align with real-world queries can significantly boost its relevance and ranking.
5. Graphical Analysis of Traffic Trends
Google employs sophisticated graphical analyses to understand and interpret search traffic patterns. This approach to data visualization aids in refining search algorithms, affecting how content is ranked.
6. Integration of AI and Advanced Analytics
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics into Google’s search algorithms marks a shift towards more intelligent, responsive search systems. This technological sophistication brings a new dimension to SEO strategies.
7. User-Centric Approach in Search and SEO
A user-centric approach is at the forefront of Google’s ranking process. This emphasis on user experience and satisfaction necessitates a focus on creating content and interfaces that resonate with and engage users.
8. Global and Cultural Considerations in Ranking
Google’s internal discussions suggest a broadening perspective, where global and cultural factors are becoming increasingly important in SEO strategies. This reflects a need for a more inclusive and diverse approach to content creation and optimization.
9. Real-Time Analysis of User Behavior
The ‘Life of a Click’ concept and the focus on user interaction signals highlight the importance of real-time analysis in understanding user behavior. This dynamic approach influences how content is perceived and ranked by Google.
10. Potential Influence of Societal Factors
The consideration of societal factors, including culture and diversity, in Google’s algorithms suggests a more nuanced approach to ranking. This indicates the growing importance of societal dynamics in SEO strategies.
These newly revealed factors from the anti-trust case exhibits offer invaluable insights for SEO professionals and content creators. They underscore the importance of staying abreast of the latest developments in SEO to craft strategies that are not only effective but also aligned with the evolving paradigms of search engines like Google.
Here is the link to all the Exhibits:
https://www.justice.gov/d9/2023-11/417508.pdf
https://www.justice.gov/d9/2023-11/417516.pdf
https://www.justice.gov/d9/2023-09/416694.pdf
https://www.justice.gov/d9/2023-09/416665.pdf
Ranking Systems Revealed by Google
Google uses automated ranking systems that consider the relevance of hundreds of billions of web pages and other content in their Search index to present the most valuable results to people who search on Google.
When Google updates its algorithms, they provide notice of these changes on its Webmaster Central Blog and other places so that content creators can make informed decisions about optimizing for them.
This is a guide to understanding some of the more notable ranking systems. It covers core ranking technologies that produce search results in response to queries and ranking needs related to specific types of searches.
1. BERT
BERT is an AI language model that helps Google better understand the context of your search, allowing it to deliver more relevant results.
BERT understands the context of a word by assessing all the other words surrounding it. Its capability to decipher the real intent of the user query leads to better search results.
Since the user’s interests are often fed in a complex format that can be hard for Google to interpret correctly, BERT helps in better understanding the intent.
Unlike traditional unidirectional language processing models, BERT uses a bi-directional language processing mechanism. It tries to understand the relationship between each word in a search query, bringing out the proper context for them and delivering accurate search results.
2. Crisis Information Systems
Google has developed systems to provide helpful and timely information during times of crisis. The information can help deal with personal crises, natural disasters, or any other widespread crisis situations.
Personal Crisis
To help people find the right resources for personal crises, Google displays information from trusted organizations on Google Search results pages, such as hotlines and other crisis resources.
SOS Alerts
In times of natural disasters or crisis situations, Google’s SOS Alert System provides updates from local, national, or international authorities. These updates may include emergency phone numbers and websites, maps, translations of useful phrases and donation opportunities.
3. Deduplication Systems
Sometimes, when you search on Google, you may find thousands or even millions of web pages that are very similar to each other. To avoid displaying unhelpful duplication, Google shows only the most relevant results.
Google also doesn’t repeat a featured snippet listing on the first page of results. This declutters the results and helps people locate relevant information more easily.
4. Exact Match Domain System
Google uses the words in domain names as one of several factors to determine if the content is relevant to a search.
However, its exact match domain system works to ensure that content hosted under domain names designed to exactly match particular queries isn’t given too much credit.
Sometimes people use exact match domain names, hoping they can rank high for a keyword in the Google search results. For example, earlier, if there is an electrician in New York City who doesn’t serve anywhere else, and his domain name is “electriciannearme.com.”, there was a probability that his domain name would pop up for a search query about electricians in any state or city.
However, with the exact match domain system update rolled out, the chances of the appearance of such results are nil.
5. Freshness Systems
Google has various systems designed to show fresher content for queries where it would be expected. For example, if there was a flood recently, news articles about the flood might appear when you search for “flood” instead of general info about its preparation and resources.
6. Helpful Content System
Google’s helpful content system is designed to show people original and helpful content written by real people, not articles written to draw traffic to a website. The Helpful Content Update is another bid by Google to make the search more user-centric.
Google’s algorithm works to improve the user experience by showing the most accurate search results possible. The Helpful Content Update has stepped up this experience and was able to put a stop to sites that have been surviving using black hat SEO techniques so far.
Consequently, websites with a large number of low-quality pages that failed to satisfy the user intent have seen a significant downfall in website traffic coming from Google due to this update.
7. Link Analysis Systems and PageRank
Google has a variety of systems that evaluate the relationships between web pages to determine which might be most helpful in response to a given query. One of these methods is PageRank, one of Google’s earliest ranking systems.
8. Local News Systems
Google surfaces relevant local news whenever required through “Top stories” and “Local news” features.
9. MUM
The Multitask Unified Model (MUM) is an AI system that understands and generates language. It’s currently used for specific applications in Search, such as to improve searches for COVID-19 vaccine information and featured snippet callouts that Google displays.
The Natural Language Processing model MUM is more powerful than BERT as it can analyze images and videos within text in 75 languages to answer complex search queries by users. With this update, a lot of focus will also fall on digital content creators and their expertise. For example, a medical content writer would find it hard to rank their content if they do not hold a medical degree or have experience writing for a medical institute.
10. Neural Matching
Neural matching is a Google AI system that gauges the relationships between concepts expressed in search queries or pages and matches them to one another.
11. Original Content Systems
Google has systems to help ensure that original content is featured prominently in search results. These include support of special canonical markup creators can use to help us better understand what is the primary page if a page has been duplicated in several places.
12. Removal-based Demotion System
Google has policies that allow the removal of certain types of content. If Google receives a high volume of requests to remove content from a specific site, it uses that as a signal to improve its results.
Legal Removals
When Google receives a high volume of valid copyright removal requests involving a given site, it uses that information to demote other content from the site in its search results. This way, if there is other infringing content on the site, people are less likely to encounter it.
Personal Information Removals
If Google detects exploitative removals of personal information from a site, it can demote content from that site in search results. In addition, Google examines other sites to see if the same pattern of behavior is happening with them and if so, it also applies demotions to those sites’ content. Furthermore, Google has automatic protections designed to prevent explicit personal images from ranking highly in response to queries involving names.
13. Page Experience System (Now Retired)
People prefer to land on pages that give them a great user experience. Google has a system that helps determine if a page gives users the experience they want, including how quickly the page loads and if it’s mobile-friendly. In situations with many possible matches, Google prefers content that provides users with a better user experience.
14. Passage Ranking System
The Passage Ranking System is an algorithm used by search engines to analyze individual sections of a web page in order to determine its relevance to a given search.
For example, if you write long-form content on technical SEO strategies and have individual sections explaining each of them, Google will rank individual sections of your content that match the search query.
This update has helped Google refine search results on a granular level and show only relevant content for which the user seeks information. So, even though the information a user is looking for is deeply buried within content, Google can bring it up in the search results using the Passage Ranking System algorithm.
15. Product Review System
The product reviews system is designed to reward high-quality reviews, content that provides insightful analysis and original research, and is written by experts or enthusiasts who know the topic well.
Google doesn’t approve product reviews that don’t talk in detail since such reviews don’t help users decide on their purchases. Although Google doesn’t penalize such sites, it has clarified that it prefers sites that publish high-quality reviews.
With the Product Review System update of 2021, sites that would still rank for poor product or service reviews earlier have stopped ranking on the search results page. Instead, this update gave a ranking boost to sites that went into great detail to review something.
16. RankBrain
RankBrain is an artificial intelligence system that helps Google better understand how words are related to concepts so that it can return relevant content even if it doesn’t contain all the exact words used in a search.
17. Reliable Information Systems
Google’s systems work in various ways, such as surfacing authoritative content and demoting low-quality content to provide the most relevant search results possible. In cases where reliable information might be lacking, Google’s systems automatically display content advisories about rapidly-changing topics or when its systems don’t have high confidence in the overall quality of the results available for the search.
18. Site Diversity System
To prevent one site from dominating all the top results, Google’s site diversity system shows no more than two web page listings from the same site in its top results. However, it may still show more than two listings in cases where its systems determine it’s especially relevant to do so for a particular search. When Google treats subdomains as part of a root domain, all subdomains and their root domain will be considered together as one site. But sometimes subdomains are treated as separate sites for diversity purposes when deemed relevant to do so.
19. Spam Detection Systems
No one wants to get junk mail in their email inbox, so spam filters greatly help. Search faces a similar challenge because the internet is full of spam that hides the most helpful and relevant information. Google fights back by using many different tools to keep out content that violates its spam policies. These tools are updated often to stay ahead of new tricks used by spammers.
20. Topic Authority System
Google recently unveiled its latest ranking system, ‘Topic Authority.’ This feature is designed to assist the algorithm in delivering relevant, expertly-written, and informative content for both Google search and news results. The ‘Topic Authority’ signal is specifically designed to assist users in finding authoritative content with accurate search suggestions.
Google states that the ‘Topic Authority’ signal plays a crucial role in presenting localized news results that cater to users. It prioritizes content from local and regional publications and emphasizes original reporting from news teams familiar with the location and topic. This system thereby enhances visibility for local publishers and those with specialized expertise relevant to a specific news story.
Moreover, Google has confirmed that the ‘Topic Authority’ system relies on certain signals to assess the credibility of a publication. These include the publication’s history and reputation for coverage on a particular topic or location, the influence of its original reporting, and its overall reputation as a source.
To succeed under the ‘Topic Authority’ system, Google advises publishers to focus on providing exceptional coverage in their areas of expertise. This aligns with Google’s ongoing initiative to promote high-quality content, and it might impact SEO strategies by placing more importance on a publication’s expertise, influence, and reputation. The introduction of ‘Topic Authority’ has resulted in a renewed emphasis on in-depth reporting and specialist journalism.
Domain Factors
1. Domain Age
Do you believe older domains gain Google’s confidence? Unfortunately, that’s not true.
In fact, Google’s John Mueller says, “domain age helps nothing”.
So, there is hardly any significance for a 2-year-old domain over a si- month-old one. While domain age is still relevant, you can’t really count on it for rankings.
2. Keyword Appearance in the Domain Name
A keyword included in your domain name is a pivotal relevancy signal.
How?
A domain name with a niche-specific focus keyword will have a competitive advantage over other domains that come without a target keyword.
3. Keyword Appearance at the Start of the Domain Name
The position of the target keyword in the domain name matters too.
Yes. A domain name that begins with the focus keyword has the edge over other sites in the same niche that feature the target keyword in the middle or end of the domain name or doesn’t include the keyword at all.
Keyword Appearance at the Start of the Domain Name
The position of the target keyword in the domain name matters too.
Yes. A domain name that begins with the focus keyword has the edge over other sites in the same niche that feature the target keyword in the middle or end of the domain name or doesn’t include the keyword at all.
4. Domain Registration Length
The time span for which a domain is registered is an important Google ranking factor.
After all, spam sites don’t last long. That’s the main reason.
According to Google,“Valuable (legitimate) domains are often paid for several years in advance, while doorway (illegitimate) domains rarely are used for more than a year. Therefore, the date when a domain expires in the future can be used as a factor in predicting the legitimacy of a domain.”
5. Keyword in Subdomain
A keyword included in your subdomain can fetch you higher search engine rankings. The SEO fraternity, including Moz’s expert panel, agrees with it.
6. Domain History
Volatile ownership is likely to signal Google to reset your website’s history, including the negation of backlinks that point to your website.
Also, if the volatile domain is penalized, the search engine may take the penalty over to the new webmaster.
7. Exact Match Domain
An exact match domain can be meritorious as long as it is of high quality and relevance.
BEWARE. If your exact match domain falls short of quality, it is likely to fall prey to a search engine penalty.
How?
The search engine has a dedicated algorithm update in place to weed out low-quality exact match domains. That’s the EMD update.
Google rolled out this update in 2012 to ensure that low-quality exact match domains don’t rank higher on search engines.
8. Public Vs. Private WhoIs
To earn Google’s trust, it is essential to reveal your identity to the search engine.
When you keep your WhoIs information private, the search engine may perceive that you have something to hide.
That will certainly affect the trust factor.
9. Penalized WhoIs Owner
What if you find a not-so-good vendor running a chain of stores at multiple locations?
You will double-check for genuineness every time, right?
That’s exactly what Google does when ranking sites.
If Google eyes a webmaster as a spammer, chances are, the search engine will meticulously scrutinize the other websites run by the same person.
10. Country TLD Extension
Do you want your website to rank higher for online searches in a specific country? If yes, you shouldn’t miss out on country-specific extensions.
Acquiring links from country-based domain extensions like .cn,.co.uk can boost your chances of achieving higher rankings in certain countries.
However, this may affect your chances of being visible in global searches.
Special Google Algorithm Rules
11. Query Deserves Freshness
Query Deserves Freshness or QDF in short, is a Google ranking algorithm that triggers the ranking of fresh web pages for certain user queries.
12. Query Deserves Diversity
Some online queries may require out-of-box results to satisfy the users and Google wants to provide diverse answers to such ambiguous queries like “Ted,” “WWF,” or “ruby.”
13. User Browsing History
Have you noticed the sites you check frequently appearing at the top of your searches?
That’s because Google takes your browsing history into consideration and gives a SERP boost to certain sites to improve the online user experience.
14. User Search History
Your search history influences the results of your future searches. That’s because Google aims to provide you with a personalized online search experience.
For instance, if you search for recipes and then for keto diet, Google is likely to offer search suggestions related to keto diet recipes for your later searches.
15. Featured Snippets
Based on a SEMrush study, a featured snippet is driven by a combination of content length, page authority, formatting, and HTTP usage.
16. Geo-Targeting
Geo-targeting refers to the process of including location information on your site. This includes local server IP and country-based domain name extension.
Google is fond of geo-targeting as it allows the search engine to fetch relevant results for user queries in a specific location.
17. Safe Search
Safe search prohibits the appearance of web pages with abusive or adult content for online search queries.
Make sure you don’t feature such profane content on your web pages to avoid being filtered out and going invisible to users.
18. “YMYL” Keywords
Google has raised the bar for Your Money Your Life (YMYL) pages.
If you are unaware of YMYL, YMYL sites are sites that feature content that can affect the health, safety and financial stability of people.
Sites offering parenting advice, medical diagnosis tips and stock market guidance are some of the best examples of YMYL sites.
Given the sensitiveness attached to these sites, the search engine has set high credibility and quality standards for them.
19. DMCA Complaints
Google always wants to help users find quality sources of information.
So, it will downrank sites that face valid DMCA takedowns or complaints pointing to copyright issues.
These takedowns denote the removal of copied content from a site or platform followed by the request of someone who owns the content.
Always make sure you publish original content to avoid copyright infringement.
20. Domain Diversity
After the so-called Big-Foot Update, the search engine has started adding more domains to each Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
21. Transactional Searches
At times, Google is likely to show different results for shopping-based keywords or search queries.
22. Local Searches and Openness
Google often displays local pages at the top for local searches and places the usual SERP results beneath them.
So, if you want to rank higher on Google for local searches, you have to create local pages and focus more on local SEO.
Google in December 2023 announced that openness is one of the local search ranking factors. This means businesses that are open during the time a user searches for non-navigational queries, have more chances of ranking in the map pack. Danny Sullivan, Google’s Search Liaison, confirmed the update.
The update primarily affects non-navigational queries, which are searches for types of services (e.g., searching for a pharmacy) rather than specific brands (e.g., searching for CVS).
The update might benefit businesses open 24/7, especially during off-hours when competitors are closed. However, Sullivan advises against altering business hours to game the system, as the signal may continue to be adjusted.
It’s important for businesses to accurately reflect their open hours in their Google Business Profile. Misrepresenting business hours could potentially lead to penalties in the future.
23. Top Stories Box
Google comes up with the “Top Stories” box for certain search terms.
For example, I enter “ Elon Musk” on Google and here’s what I get.
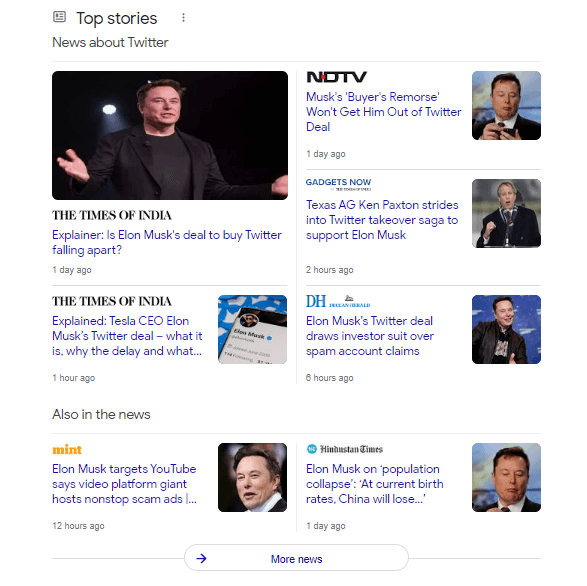
24. Big Brand Preference
Following the Vince update (interlink Vince update) in 2009, Google gave top brands a SERP boost for a certain set of search terms.
25. Shopping Results
The search engine is likely to come up with shopping results for some selected keywords.
That said, choosing your keywords wisely can help improve your conversion rate and boost sales.
26. Image Results
For some searches, Google will show images in its organic search results.
That’s you should include appropriate images on your web pages and NEVER overlook image SEO, especially when you want to rank #1 on Google.
27. Easter Egg Results
While Google has answers for every user query, at times, the search engine may mislead you with inappropriate results. These results are widely called “Easter Egg Results” by the SEO community.
In such cases where you find yourself fooled, you can raise a query on Victor PanVictor Pan’s Twitter page.
28. Single Site Results for Brands
Your brand is your online identity. That’s why creating brand awareness among your target audience is important.
Google often fetches results from the same site for domain or brand-based search terms.
29. Payday Loans Update
Google weeds out very spammy queries with the specially designed algorithm update called the payday loans update.
According to Google, this update affects “different languages to different degrees”. That means a language with higher web spam will face more consequences with this algorithm update than the ones that see minimal web spam.
Brand Signals
30. Branded Anchor Text
Branded anchor texts are unique to your brand and they send stronger ranking signals to the search engine than generic keywords.
This will help you achieve higher search engine rankings.
That’s why it is critical to position your brand better and gain brand mentions across the internet.
31. Branded Search
People often search for well-established brands on the internet.
So, when users search for your brand online, Google confirms that your brand is real. This can boost the credibility of your brand.
32. Facebook Page and Likes
Real brands are likely to have Facebook pages with lots of likes and Google takes them seriously.
So, if you have an official Facebook page for your brand to complement your online presence, it’s good. However, you also have to attract enough followers to get more Facebook likes..
33. Brand + Keyword Searches
Do people use your brand name along with other keywords or search terms? If yes, you hit the jackpot.
If users search for “Stan Ventures Google algorithm updates” or “Stan Ventures link building guide”, for example, Google will improve the rankings for corresponding web pages and pull them up on SERPs when people use the same search term without the brand name. In this case, Stan Ventures is likely to rank higher for the search terms “algorithm updates” and “link building guide.”
34. Twitter Profile with Followers
Just like Facebook, Twitter is another great platform to strengthen your brand presence.
If your brand has a dedicated Twitter page with lots of followers, Google eyes you as a popular brand and that improves your chances of ranking higher.
35. Official LinkedIn Company Page
LinkedIn is one of the top professional social networking platforms.
That said, the presence of an official company page representing your brand on LinkedIn will speak to the search engine for your credibility.
36. Known Authorship
Author credit adds to the authenticity of your content. This will help you achieve better SERP rankings than web pages without proper author claims.
That was, in fact, stated by Eric Schmidt, the former CEO of Google, in 2013.
Given the scenario, make sure you include an author bio in your blogs and articles in order to boost your chances of outranking your competitors.
37. The Legitimacy of Social Media Accounts
Let’s take the social media accounts of two different brands. Brand A has 15,000 followers, but the account displays just 3 or 4 posts with very minimal to no engagement. On the other hand, Brand B also has 15,000 followers but has a decent number of posts at regular intervals with a good interaction rate.
B sounds genuine, right?
Google has, in fact, filed a patent to evaluate if social media accounts are real or fake.
38. Brand Mentions on Top Stories
Popular brands often make it to Top Stories on Google. Some really big brands occupy the whole news feed on Google’s first page.
That again nails the importance of building a brand for SEO.
39. Unlinked Brand Mentions
Brands do get mentioned online without being linked to.
Google considers these unlinked brand mentions as a brand signal.
40. Brick and Mortar Location
Real businesses often have offline workspaces. That said, it is likely that Google will look for locations on a website to find out if a brand is real or not.
Page-Level Factors
41. Keyword in Title Tag
Placing keywords in the title tag not only increases your website’s SEO value but also fuels your click-through rate and brings more traffic to your site.
Also, keywords in the title tag help the search engine and users alike to understand what your web page is about.
42. Title Tag Starting with Keyword
According to Moz, a title tag with a keyword at its beginning will both perform better on organic SERPs and witness a higher click-through rate than the title tags that come with keywords in the middle or end.
43. Keyword in Description Tag
Google doesn’t consider the meta description tag as a direct ranking signal.
But then, keyword appearance in the meta description can trigger the click-through rate when your web page appears on SERPs.
CTR is, of course, an important ranking factor, which in turn, makes keyword placement in the meta description essential.
44. Keyword in H1 Tag
H1 tags are another important signal second only to title tags.
Apart from title tags, Google also takes H1 tags into consideration to determine the relevance of your content to user search queries.
45. TF-IDF
TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) denotes finding out how often a particular word occurs in a piece of content.
The more often the word appears on a page, the higher the chances that the page is about the specific word.
Google leverages TF-IDF with AI to figure out what a page is about.
46. Content Length
Google is likely to prefer long-form content more than short-form content.
Why?
That’s because long-term content tends to cover topics in detail and provide more information related to search queries.
At the end of the day, improved user experience is what really matters for Google.
47. Table of Contents
Putting up an internally linked table of contents will help Google to comprehend your content quicker and better.
Besides, it also increases the chances of your content appearing in snippets results in organic SERPs, which, in turn, boost your CTR.
48. Keyword Density
Keyword density refers to the frequency of a search term appearing in your content.
While keyword density isn’t as important as it used to be, it still allows Google to understand your content and determine its relevance.
49. Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords in Content (LSI)
LSI keywords help Google to comprehend the contextual meaning of words with multiple meanings.
These keywords are a great content quality signal.
50. LSI Keywords in the Title and Description Tags
The inclusion of LSI keywords allows the search engine to make better sense of the words in title tags and description tags.
They may also act as a content quality signal.
51. Page Covers Topics In-Depth
Again, providing users with more relevant information is Google’s priority every single time.
So, the search engine is naturally more fond of pages that cover a topic in detail than the ones that discuss only parts of it.
52. Page Loading Speed via HTML
Page speed is a SUPER-important ranking factor not just for Google but also for Bing.
Search engine spiders find out your page loading speed by your web page’s HTML codes.
53. Page Loading Speed Via Chrome
Apart from HTML codes of a web page, Google also leverages Chrome user data to estimate the page loading speed.
54. Use of AMP
Though Accelerated Mobile Page (AMP) load doesn’t directly impact search engine rankings, it would still come in handy to achieve improved SERP results on mobile devices.
55. Entity Match
If a web page matches the entity the user is looking for online, the page is likely to get a SERP boost for that particular keyword.
56. Google Hummingbird
The Hummingbird update helped the search engine look beyond just keywords. With this algorithm update, Google could decode the topic of a web page with improved precision.
57. Duplicate Content
The presence of identical or duplicate content within a website can have an adverse effect on its search engine visibility.
Make sure you eliminate duplicate content to safeguard your website’s health.
58. Rel=Canonical
When two or more pages on your website contain identical content, you can use canonical tags to dodge a search engine penalty.
Canonical tags are a way of telling Google which one of those pages is original. This way, the search engine bots index and rank one particular page ignoring the rest.
59. Image Optimization
Optimizing the images on your website is as important as optimizing your content, title tags and meta tags.
The file name, alt text, title, description and caption of the image you upload send relevancy signals to the search engine.
60. Content Recency
Google chooses to display recently published or refreshed content at the top of SERPs. This is especially true for time-sensitive online searches.
For some pages, Google also shows the date the content was last updated.
61. The Magnitude of Content Updates
Google doesn’t just prioritize refreshed content. It also has a keen eye for the presence of the most recent information in the same.
After all, outdated content with some tweaks isn’t what the search engine giant really expects.
The more fresh and unique your content is, the better your chances of securing a top slot on search results.
62. Historical Page Updates
How often do you update your web pages?
The frequency of page updates also drives the freshness factor.
63. Keyword Prominence
It gives you an edge when your keyword appears within the first 100 words of your content. That way, your page will soar higher on SERPs in terms of relevance.
64. Keyword in H2, H3 Tags
Are you using your target keyword in your H2 and H3 tags? That’s a WRONG move. When you do so, it brings down the chances of your web page ranking for relevance.
So, how do you fix this?
It’s simple. Use LSI keywords in your H2 and H3 tags.
65. Outbound Link Quality
Linking to high-authority sites in your niche fetches you high-quality outbound links. These outbound links send strong trust signals to Google.
So, make sure you build powerful outbound links that help you be in Google’s good books.
66. Outbound Link Theme
Google is likely to leverage the content of the web pages you link to as a relevancy signal. That’s precisely why you should link to niche-specific sites that share a common customer base with you.
If not, chances are, Google may perceive your page to be something it is not. That way, the search engine might NOT pull your page up on SERPs when your potential customer performs a search.
67. Grammar and Spelling
Proper grammar and spelling are a content quality signal.
Content that rightly aligns with the rules of grammar and spelling often qualifies as good content.
68. Syndicated Content
Are you sure your content is original and unique?
Content copied from other web pages that are already indexed is plagiarized.
Google will NOT rank pages that feature plagiarized content. After all, the search engine bots will NEVER index them at all.
69. Mobile-Friendly Update
Post the Mobilegeddon algorithm update in 2015, web pages properly optimized for mobile devices are at a competitive advantage and rank better.
70. Mobile Usability
Google’s mobile-first index prioritizes web pages that are easily accessible for mobile users over the ones that aren’t mobile-friendly.
71. Hidden Content on Mobile
Pages with hidden content on mobile devices are at risk of going unindexed or may not be taken into consideration as heavily as content that’s fully visible.
72. Helpful “Supplementary Content”
Basically, supplementary content is anything that prompts the user to visit the other pages on a site. This includes internal links, related blog posts or articles and related products.
Supplementary content is an indicator of the quality of a web page and that makes it a Google ranking factor.
73. Content Hidden Behind Tabs
Do your visitors have to click on tabs to access content beneath it?
If yes, Google may not index that content.
74. The Number of Outbound Links
Don’t overuse outbound link building. Too many do-follow outbound links can negatively impact your site and affect your SERP positioning.
75. Relevant Images
Multimedia elements, including images, and videos are a significant content quality signal.
Make sure you include these elements in appropriate places of your content to enhance its quality and achieve higher search engine rankings.
76. Number of Internal Links Pointing to Page
Internal links are a good way of telling Google how important a web page is. The more the number of internal links, the more the importance attached to the page.
Make sure you create robust internal links to a page from your other web pages using appropriate anchor texts.
Internal links are a great relevancy signal and can fetch remarkable outcomes, especially when used right.
77. Quality of Internal Links Pointing to Page
Internal links from powerful pages on your page produce a stronger impact than the links from pages with a low PageRank or no PageRank at all.
78. Broken Links
Are there too many broken links on a page? That often means the page is neglected.
The probability of such neglected pages ranking on SERPs is very low.
In fact, the Google Rater Guidelines Document considers broken links as one of the ways to determine the quality of the homepage.
That said, it is critical to fix broken links at the earliest to improve your site’s health and SERP standing altogether.
79. Reading Level
Google certainly assesses web pages based on readability. After all, your content has to be comprehensible for your visitors and that’s what drives traction.
Pages with high readability are likely to be ranked higher on Google than the ones that are less readable.
80. Affiliate Links
Google isn’t a fan of hardcore affiliate sites. While a few affiliate links won’t harm your website, too many of them will.
The presence of a lot of affiliate links on a site prompts the search engine bots to examine the site for other quality signals to determine its ranking.
81. HTML Errors/W3C Validation
Clumsy page coding results in poor user experience. So, sloppy HTML codes are a red flag that points to low-quality sites.
Be very cautious to avoid HTML code errors and save your site from slipping down on search engine results.
82. Domain Authority
Domain authority is measured on a scale of 1 to 100. The higher the authority, the more powerful the domain.
Pages on high authority domains usually rank higher than the pages that belong to a site with low domain authority.
83. Page’s PageRank
Pages with high authority are likely to outperform pages with not much link authority on Google’s search results.
84. URL Length
The length of page URLs matters.
Studies claim that short URLs have an edge when it comes to search engine results. On the contrary, excessively long URLs hamper your search engine visibility.
85. URL Path
A page that’s closely associated with the homepage may get a slight SERP boost compared to the other pages that lay deep down in the site’s architecture.
86. Human Editors
Though it’s never official, it is claimed that Google has filed a patent for a system where human editors can possibly influence SERPs.
87. Page Category
Page category is yet another relevancy signal.
A web page grouped under a relevant category is likely to get a relevancy boost, while a page filed under an inappropriate category doesn’t.
88. Keyword in URL
While some people perceive the appearance of keywords in the URL as a minor ranking factor, every Google ranking factor is important to make it to the top of the search engine and so is this one.
89. URL String
Google reads URL strings to better comprehend what a web page talks about and takes it into consideration when ranking pages.
90. References and Sources
Listing down references and sources for content is an indication of high-quality content.
As per the Google Quality Guidelines, reviews are supposed to have an eye for citations, references, and sources when weighing web pages that demand field expertise.
However, the search engine also makes it a point that these external links are NOT ranking signals.
91. Bullets and Numbered Lists
Numbers and bullets come in handy to break your content into chunks in order to make it more readable and comprehensive for your target audience.
As the technique is user-centric, Google likes it when you use bullet points and serial numbers in your content.
92. Priority of Page in Sitemap
A sitemap is your website’s blueprint that allows the search engine bots to crawl, index and rank your sites faster.
Using a sitemap(sitemap.xml), you can tell Google which of your site pages are important. This way, your sitemap can influence indexing and ranking based on predefined page priorities.
93.Too Many Outbound Links
As I mentioned earlier, using too many outbound links isn’t advisable.
Excessive outbound links are likely to overshadow the main content of a web page and make way for distraction.
94.UX Signals From Other Keywords a Page Ranks For
Is your web page ranking for many keywords at once? Cheers!
Google looks at pages ranking for multiple keywords as a quality signal as it can deliver value to several users with different search queries.
95. Page Age
Page age counts as a Google ranking factor.
Wait. But Google likes fresh content, right?
Yes, However, an older page whose content is updated on a frequent basis can still outrank a new page.
After all, Google has its ways.
96. User-Friendly Layout
Never overlook your website’s layout design.
According to Google’s Quality Guidelines, high-quality web pages with a frictionless page layout can make the main content quickly visible to the users.
97. Parked Domains
A parked domain is a domain that is registered but stays inactive without being connected to a hosting server.
After an algorithm update in December 2011, the online visibility of parked domains has come down.
98. Useful Content
According to SEO Roundtable, high-quality content isn’t necessarily useful content.
So, chances are, Google will differentiate between high-quality content and useful content to rank pages in its index.
User Interaction
99. RankBrainTime
RankBrain is a machine-learning algorithm that allows Google to process and organize search results.
It is believed that RankBrain measures how users interact with search results.
100. Organic Click-Through Rate for A KeywordTime
According to Google, organic CTA and SERP ranking go hand in hand.
With the increase in CTA, the SERP rank of the web page also increases for the given keyword.
101. Organic CTR for All KeywordsTime
The organic click-through rate of all the keywords a site ranks for is a user-interaction signal and it fetches a quality score for organic results.
The higher the quality score, the better it is for your search engine visibility.
102. Bounce RateTime
Your website’s bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your site without taking any action. The impact of bounce rate on SEO is questionable until now.
But why would someone want to leave your site without performing an action if it meets their expectations?
So, in a way, an increased bounce rate is a sign of poor user experience.
That’s why bounce rate is not something you can take lightly when it comes to SEO.
103. Direct TrafficTime
Google uses Chrome data to determine how many people visit a site and how often they do.
Websites that generate high direct traffic are likely to meet higher quality standards than the ones that receive very little direct traffic.
104. Repeat TrafficTime
If a site witnesses several returning visitors on a frequent basis, Google will consider it a high-quality, user-engaging site.
This helps fuel the site’s search engine ranking.
105. Pogo StickingTime
Pogo sticking is a kind of bounce where the user clicks on a result on SERPs but leaves the site immediately only to click on another search engine result.
As user exit happens so quickly, pogo sticking will harm your site.
106. Blocked SitesTime
There was a time when Google would block sites that fell short of the quality score, offering no SEO benefit to those sites.
However, Google has now disabled this feature on Chrome.
107. Chrome BookmarksTime
As you may know, Google counts on Chrome user data to determine the popularity of web pages.
Pages that are bookmarked on Chrome are looked at as direct traffic and are likely to get a SERP boost.
108. The Number of CommentsTime
The number of comments your content evokes is an indication of user interaction.
While comments signal that the content is useful and user-engaging, the SERP rank for the particular page will increase.
109. Dwell Time
Dwell time is the amount of time visitors landing on your page from Google search spend on that specific page.
Dwell time helps Google to determine the performance and quality of your page. The higher the dwell time, the better your SEO ranking.
On-Site Webspam Factors
110. Panda Penalty
Google’s Panda update hits low-quality sites with a search engine penalty and holds them back from securing better search engine ranking.
111. Links to Bad Neighborhoods
Being associated with spammy sites can reduce your credibility in the eyes of the search engine giant and may bring down your search rankings.
So, it is essential to make sure you don’t link out to low-quality or spammy sites with a bad track record.
112. Redirects
If Google detects sneaky redirects, it will not only penalize the site but also de-index it. That’s a big blow for a webmaster.
Given the kind of impact devious redirects can create, it’s wise to avoid them.
113. Pop-ups
According to the Google Rater Guidelines, Google reserves the right to penalize sites that display unnecessary pop-ups and distracting ads.
After all, these pop-ups and ads hinder a smooth user experience online.
114. Interstitial Pop-Ups:
Google also penalizes sites and individual pages that show up full-page pop-ups for mobile users.
These full-page pop-up ads on mobile versions of websites stop users from accessing the page’s content easily.
115. Site Over-Optimization
Overdoing has its drawbacks and this holds true for search engine optimization as well.
Over-optimization, including keyword stuffing, excessive keyword decoration and header tag stuffing, can bring a Google penalty for sites, which, in turn, brings them low rankings.
116. Gibberish Content
Google can detect gibberish content and that allows the search engine to weed out auto-generated or spun content when indexing web pages.
117. Doorway Pages
Sometimes, a page may redirect users to a page that’s different from the page they want to land on. Such a page is called a doorway page.
Google hates doorway pages as it perceives them as attempts to manipulate its algorithm. The search engine never endorses sites that aim to rank higher using unfair means.
118. Ads Above the Fold
The appearance of ads above the fold can annoy users.
With its Page Layout algorithm, Google penalizes sites that display too many ads above the fold.
119. Hiding Affiliate Links
Google doesn’t like shady practices.
That said, if the search engine finds out you are hiding or cloaking affiliate links from its eyes, it will penalize your site.
120. Fred
Launched by Google in 2017, the Fred update tends to punish sites that prioritize money-making over delivering value to users.
121. Affiliate Sites
Google doesn’t endorse affiliate sites because these sites operate with money-making as their primary motive.
That’s why Google watches sites that prefer money-making to user engagement closely and tightens scrutiny over them.
122. Auto-Generated Content
Google has an aversion to spun content.
Once it finds out a site has published auto-generated content, the search engine is likely to bury the site deep down in SERPs by imposing a massive penalty.
In the worst-case scenario, it may deindex the site, so it doesn’t appear on Google search results at all.
123. Excessive PageRank Sculpting
PageRank sculpting is a practice where you no-follow a majority of outbound links on your page in order to pass PageRank juice to selected outbound links.
If you go too far with PageRank sculpting, you will fall prey to the search engine for manipulating its algorithm.
124. Meta Tag Spamming
Adding keywords to your title and meta tags can boost your organic CTR.
However, if Google finds out that you intentionally include keywords in your title and description tags to trick the search engine into rewarding your page with high rankings, it may backfire and you are likely to end up with a penalty.
125. IP Address Flagged as Spam
If the IP address of a server is marked as spam, all the other sites on the particular server will get affected.
Off-Site Webspam Factors
126. Hacked Sites
Hacked sites are likely to be dropped from search engine results.
In fact, Search Engine Land was once deindexed and lost its rankings when it looked like the site was hacked.
127. Unnatural Influx of Links
An unnatural influx of links that happens with no warning is a sure-shot indication of spammy links.
128. Penguin Penalty
Google’s Penguin algorithm spots sites with unhealthy links and imposes a search engine penalty on them by bringing down the SERP rankings of their web pages.
129. Link Profile with a High Percentage of Low-Quality Links
Several links from sources that are usually used for black hat SEO are a sign of cheating the system.
It includes forum profiles, blog comments and more.
130. Links From Unrelated Websites
Lots of backlinks from websites that are topically unrelated can increase the chances of ending up with a manual penalty.
131. Unnatural Links Warning
It is often a sign of a drop in SERP rankings when Google notifies you of “Google Search Console notice of detected unnatural links” messages.
132. Low-Quality Directory Links
If you keep getting links from low-quality directories, your website is at a high risk of being penalized by Google.
133. Widget Links
Google doesn’t like it when webmasters embed a widget on their site in order to prompt auto-generated links.
134. Links from the Same Class C IP
Getting bulk links from sites on the same server IP isn’t really a good idea. That will certainly tell Google that all your links are generated from a blog network.
135. “Poison” Anchor Text
The name should tell you how harmful it is for your dear website.
If you have “poison” anchor text, including pharmacy keywords pointing to your website, it can potentially be an indication of spam or a hacked site and may lower your site’s ranking.
136. Unnatural Link Spikes
As per a Google Patent from 2013, Google can identify if the influx of links to a site is valid or not. Upon finding the illegitimacy of links, they won’t be of any value at all.
137. Links From Articles and Press Releases
Following the misuse of article directories and press releases to earn links, Google now looks at these as a “link scheme” in most cases.
138. Manual Actions
While there are many types of manual actions, the search engine giant mostly uses them to target link building with black hat SEO techniques.
139. Selling Links
If Google discovers that you are selling links, the online visibility of your site will face a negative impact.
140. Google Sandbox
Newbie sites that get links in massive quantities of links are subjected to the Google Sandbox. This will prevent the particular site from being visible online on a temporary basis.
141. Google Dance
If Google suspects that you are gaming with its algorithms, it is likely to implement a Google patent termed ‘SERP Dance’ to bring momentary fluctuations in your search rankings.
142. Disavow Tool
The disavow tool makes way for lifting up algorithmic or manual penalties that fall on sites to create a negative SEO impact.
143. Reconsideration Request
A well-targeted reconsideration request is likely to remove a search engine penalty that hurts your website’s SEO.
144. Temporary Link Schemes
Google can sense it when people indulge in temporary link schemes that involve building and removing spammy backlinks quickly.
Site-Level Factors
146. Content Providing Value and Unique Insights
Google hates it when content doesn’t offer any value or insights to users. It punishes such no-value pages with a penalty.
Thin affiliate sites that focus blatantly on money-making are often subjected to a search engine penalty.
147. Contact Us Page
Google uses your contact information to confirm your site’s credibility.
From Google Quality Guidelines, it is clear that the search engine prioritizes sites that furnish reliable contact information.
Ensure that your contact details are aligned with your WhoIs information.
148. Domain Trust / TrustRank
A vast majority of the SEO community believes that “TrustRank” is a crucial ranking factor as the trust factor has the edge over Google rankings.
149. Site Architecture
A good site architecture can bolster your SEO efforts while making way for a thematic organization of your website’s content.
Besides, it also helps Google bots to discover your content easily to crawl, index and rank your web pages.
150. Presence of Sitemap
With a sitemap in place, you can facilitate your visitors to make better sense of your website and navigate through it without any hassle.
For Google, the sitemap helps locate important pages quickly. This will fuel more efficient indexing and ranking and boost your search engine visibility.
151. Site Uptime
Be it server maintenance or other server issues, an increase in the frequency of downtimes can potentially affect your site’s rankings. In some cases, pages may even be de-indexed.
So, make sure you find ways to cut down site downtimes and protect your site from facing Google’s wrath.
152. Server Location
Your page may secure different search engine rankings in different places based on your server location.
This is particularly beneficial when it comes to location-based searches.
153. SSL Certificate
Following Google’s confirmation, HTTPS has become a definite ranking factor with no room for doubt,
While Google also claims that it will only be a tiebreaker, it is as important as the other factors for people who don’t want to miss out on any possible Google ranking factor,
154. Terms of Service & Privacy Pages
These two landing pages help Google determine how trustworthy a site is. They also influence the E-A-T of the site.
155. Duplicate Meta Information On-Site
The presence of excessive duplicate meta information isn’t a good sign, especially because it may lead to a decrease in the online visibility of your page.
Take appropriate actions when the search console warns you about the existence of lots of duplicate meta information and dodge bigger consequences.
156. Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumb navigation is a user-friendly navigation technique that allows users and the search engine alike to figure out where exactly they are on a site.
According to Google, Google search leverages breadcrumb markup to categorize the information from a specific page in SERPs.
157. Mobile-Optimized
Since a vast majority of users today use mobile phones to search for something online, Google is particularly fond of web pages that are optimized for mobile devices.
Besides, Google may penalize sites that aren’t mobile-friendly.
158. YouTube
Google offers a special place for YouTube videos on search results.
Search Engine Land has observed that there’s a significant traffic boost for YouTube after Google’s Panda update.
159. Site Usability
When users find it difficult to use or navigate through your site, chances are, the bounce rate will spike and the dwell time will go down.
That may indirectly contribute to a drop in your rankings.
160. Using Google Analytics and Google Search Console
Google Analytics and Google Search Console are two primary tools that supply Google with more data to index and rank sites better.
While Google says it’s a myth, many people believe that these two tools influence search engine rankings enormously.
161. User reviews/Site reputation
User reviews on sites like Yelp.com play a vital role in determining your site reputation.
In fact, Google disclosed a candid outline to demonstrate how it uses online reviews followed by a website exploiting its customers to earn more links and press.
Backlink Factors
162. Linking Domain Age
Earning backlinks from older domains will help you build a more powerful backlink profile than gaining links from new domains.
163. The Number of Linking Root Domains
Google takes into account the number of referring domains (the domains that link out to a particular site) when ranking sites.
164. Number of Links from Separate C-Class IPs
When you earn links from separate class- C IP addresses, you witness a wider breadth of sites linking out to you. This may help you boost your site’s rankings.
165. Number of Linking Pages
The search engine gives importance to the total number of linking pages, including the ones from the same domain.
166. Backlink Anchor Text
According to Google, anchor texts provide more accurate information about a page than the page itself.
While over-optimized anchor texts act as a webspam signal, keyword-rich anchor texts can be a source of strong relevancy signals.
So, Choose your backlink anchor text wisely.
167. Alt Tag (for Image Links)
ALT Text is often the anchor text for images.
Make sure you include a focus keyword in your anchor text to reap SEO benefits.
168. Links from .edu or .gov Domains
Google says that it ignores a lot of .edu sites. Also, Matt Cutts once said that TLD doesn’t influence a site’s importance.
However, SEO experts believe that .gov, .edu, and .tld links still occupy an important slot in Google’s algorithm.
169. Authority of Linking Page
The PageRank of the referring web page has always been an important Google ranking factor. Ensure you link back to authoritative pages in a referring domain.
170. Authority of Linking Domain
The authority of the domain linking out to your site is likely to play a vital role in deciding your link value and ultimately your SERP rankings.
171. Links from Competitors
Gaining backlinks from sites that compete with you on SERPs can give you an edge and help you position yourself as a more authoritative source in your industry.
172. Links from “Expected” Websites
While this is still controversial, chances are, Google will not completely trust your site unless you link back to certain expected domains in your niche.
173. Links from Bad Neighborhoods
Building links to spammy or low-quality domains will fetch a negative SEO impact and affect your Google search rankings.
174. Guest Posts
Guest post links are a valuable addition to your link profile. However, truth be told, guest post links aren’t as powerful as genuine editorial links. But there are genuine blogger outreach agencies that do manual outreach and connect with bloggers to build backlinks.
Too many guest postings on low quality sites will bring you problems.
175. Links from Ads
Google prefers links from ads to be no-followed or to come with the rel=sponsored attribute.
However, there are possibilities that the search engine will filter and see value in do-follow links generated from ads.
176. Homepage Authority
The homepage is the most important page on a site. So, it is essential that you gain backlinks from powerful domains in your niche in order to boost your homepage authority considerably.
177. NoFollow Links
As Google doesn’t follow nofollow links, these links don’t pass link juice to your site. But still, they can fetch qualified referral traffic to your website.
Also, achieving a balance between do-follow and nofollow links is crucial to building a natural and healthy link profile.
That said, nofollow backlinks indirectly contribute to strengthening your SERP position.
178. Diversity of Link Types
It may look unnatural if you get too many links from a particular domain.
On the other hand, it is a good sign when you get one link each from multiple domains. This way, you can create a more natural and authentic link profile.
179. “Sponsored” or “UGC” Tags
Google eyes links that come with a “rel=sponsored” or “rel=UGC” attribute differently than it perceives a do-follow or no-follow link.
180. Contextual Links
The search engine uses contextual links to evaluate not just your site but also the site that links out to you.
That’s why it is important to ensure that the content wound around the link is of high quality. If you meet this parameter, Google is likely to give your page a high SEO value.
181. Excessive 301 Redirects to Page
Backlinks that point to 301 redirects can potentially affect your PageRank.
182. Internal Link Anchor Text
Internal link anchor text is yet another relevancy signal. However, internal links have a lesser weightage compared to anchor text coming from external sites.
183. Link Title Attribution
Link title is the text that you see when hovering over a particular link. Link title attribution offers more information about the link and delivers value to users.
184. Country TLD of Referring Domain
If you own a country-specific website, building backlinks from leading country-based domains specific to the same country as yours will help you achieve better search visibility and higher rankings in that location.
185. Link Location In Content
The SEO value you get from links depends on where you choose to place your link in the content.
Link placement in the first paragraph of the content, especially in the beginning, fetches a higher SEO value than placing it towards the end of the paragraph.
186. Link Location on Page
When you build backlinks, you need to make it a point that your link is placed in a location where it is easily visible to users.
Placing the link in your content fetches better results than placing it in the footer or sidebar.
187. Linking Domain Relevancy
A link that you earn from a domain related to your niche brings more value than a link coming from a domain that doesn’t share a common niche.
188. Keyword in Title
Google likes it when you build links from pages that contain your page’s target keyword in the title.
189. Page-Level Relevancy
A backlink from a relevant page is likely to pass on more value to your page.
190. Positive Link Velocity
A positive link velocity indicates that your site is increasing in popularity and also brings a SERP boost.
191. Negative Link Velocity
Negative link velocity is just the exact opposite of positive link velocity. It shows that your website is going down in terms of popularity and decreases SERP rankings.
192. Links from Hubpages
As per the Hilltop Algorithm, building links from hubpages that feature rich resources for any particular topic brings more value to your site.
193. Link from Authority Sites
Backlinks from high authority sites are likely to pass more link juice to your site than links from similar sites with minimal authority.
194. Linked to as Wikipedia Source
While Wikipedia links come with a no-follow attribute, SEO experts still opine that Google looks at Wikipedia links as a strong source of authority.
195. Co-Occurrences
The words that sit around a backlink play an imperative role in decoding to Google what the target page is about.
That’s why the content surrounding your backlink should be more relevant and crafted to perfection.
196. Backlink Age
As per a Google patent, older backlinks are more powerful than newer links, especially when it comes to determining the search rankings of a site.
197. Links from Real Sites vs. “Splogs”
As a rule of thumb, the search engine gives more importance to real sites with genuine traffic than spam blogs.
Google uses brand and user interaction to determine the weightage of these links.
198. Natural Link Profile
A website that’s backed by a natural link profile has better chances of ranking higher on Google than a site that relies on black hat techniques to build links.
Striking a perfect balance between your do-follow and no-follow links is one of the best ways to strengthen your link profile and give it a natural flair.
199. Reciprocal Links
Going too far with link exchanging is viewed as an unfair link scheme by Google. It may affect your website’s SEO.
200. User-Generated Content Links
Google can certainly distinguish between user-generated content links and links from content published by webmasters on real sites.
Never resort to such unfair techniques to add more links to your link profile. Google doesn’t encourage that.
201. Links from 301
Even Though Matt Cutts once said that 301 redirects are similar to backlinks, the SEO community believes that 301 redirects are likely to lose some link juice in comparison to direct links.
202. Number of Outbound Links Within a Page
A backlink on a page with too many outbound links is likely to pass a lower PageRank to the target site than a link on a page with fewer external links.
203. Forum Links
Google considers links from forums highly spammy and may devalue them significantly.
204. Word Count of Linking Content
Word count does matter for link building.
For example, a link from a 1000-word long content is more significant than a link placed in a short snippet.
205. Schema.org Usage
Web pages that support microformat are likely to outperform pages that come without them.
206. TrustRank of Linking Site
The TrustRank a link can pass on to your site depends heavily on how trustworthy the referring domain is in the eyes of Google.
207. Sitewide Links
As confirmed by Matt Cutts, sitewide links are usually compressed to constitute a single link.
208. Quality of Linking Content
Links that are generated from high-quality, user-engaging content are much more valuable than links that come from spun or machine-generated content.
Retired Ranking Systems
The below systems are being kept for historical purposes. They’ve either been incorporated into successor systems or made part of Google’s core ranking systems.
1. Hummingbird
Google’s Hummingbird update was a significant change to Google’s overall ranking systems made in August 2013. The search engine giant has continued to make changes to its ranking systems since then.
2. Mobile-friendly Ranking System
In situations where there are many possible matches with relatively equal relevancy, the mobile-friendly ranking system gave preference to pages that display better on mobile devices. The system has since been incorporated into Google’s page experience algorithm.
3. Page Speed System
The page speed update, announced in 2018 and originally meant to boost mobile search results, has become part of Google’s page experience system.
4. Panda System
It was designed to ensure high-quality and original content appeared in Google’s search results. Announced in 2011 and given the nickname “Panda,” it evolved into one of Google’s core ranking systems in 2015.
5. Penguin System
This was a system designed to combat link spam. Announced in 2012, it was integrated into Google’s core ranking systems in 2016.
6. Secure Site System
In 2014, Google announced that it would boost secure websites in its search results. HTTPS had been in use for some time, but it was still uncommon at that point. Google’s move effectively encouraged the use of HTTPS and made it easier for site owners to implement. The ranking boost is now part of Google’s page experience system.
7. Page Experience System
Google had the page experience system in place to determine the kind of experience a page offers the users and that included signals like Core Web Vitals, mobile friendliness, HTTPS and no intrusive interstitials.
So, do these signals still influence Google Search rankings?
Google says, “While not all of these may be directly used to inform ranking, we do find that all of these aspects of page experience align with success in search ranking, and are worth attention.”
Now what does it mean for the Page Experience Update?
Again from Google, “The page experience update was a concept to describe a set of key page experience aspects for site owners to focus on. In particular, it introduced Core Web Vitals as a new signal that our core ranking systems considered, along with other page experience signals such as HTTPS that they’d already been considering. It was not a separate ranking system, and it did not combine all these signals into one single “page experience” signal.”
If you are wondering what’s the drive behind this change, here’s what Google’s Mueller says. “We’ve seen people hyper-focus on these numbers, that’s not a good use of time & energy.”
It looks like while not all the page experience metrics may influence search rankings directly, they may still be worth paying attention to.
Get Your Free SEO Audit Now!
Enter your email below, and we'll send you a comprehensive SEO report detailing how you can improve your site's visibility and ranking.

You May Also Like
Turnaround Time (TAT) for SEO Projects: How Agencies Set Expectations
As an agency owner, the key to delivering a faster ROI for your clients is promptly implementing the proper SEO strategies. However, managing hundreds of client websites simultaneously means each client expects rapid results. That’s why your SEO agency must set clear expectations about turnaround time (TAT) with your clients, ensuring they understand the process … Turnaround Time (TAT) for SEO Projects: How Agencies Set Expectations
6 SEO Pricing Models for Agency Owners
When it comes to SEO service pricing, it can be difficult to know what is a fair price and what is too much. Read this blog to know more.
What’s a Good Click-through Rate?
Checkout some of the most effective ways to improve the CTR (Click Through Rate) which is one of the hidden search engine ranking factors.









Comments