Mixed Content Error: What Is it And How to Fix It?
By: Dileep Thekkethil | Updated On: January 23, 2024
Table of Contents
By now you must have enabled HTTPS on your server. Great.
If not, don’t worry, you can do that anytime by contacting your hosting provider or by installing a WordPress plugin like Really Simple SSL.
I recommend enabling HTTPS because Google has been showing greater affinity to rank websites that are secured.
So, now that you have enabled HTTPS, the Chrome browser must recognize your site as secure, right?
Not necessarily!
If you are still seeing an unsecured connection while opening your website, that means you have Mixed Content Error.
The usual culprit behind this is your Java, CSS stylesheet, and images, which are being delivered from an unsecured server or http servers.
The Chrome Update that was launched in December 2019 started displaying the mixed content issue and it continues.
Before the update, Google had to recommend webmasters adopt HTTPS instead of HTTP to ensure the safety of its users.
The HTTPS factor is now one of the 200 ranking signals, and Google officials have confirmed the same.
Now, Google wants to tighten up things further as it has asked webmasters to ensure that their HTTPS domains are not rendering mixed content.
Users will be notified about the use of mixed content on any affected page, and they can either choose to back out or continue browsing the page after agreeing to the notification.
That said, the majority of users who see a “not secured page” notification get dissuaded from spending further time on the page.
This might lead to a high bounce rate and can negatively affect the site’s ranking on the Search Engine Results Page.
The SEO fraternity has widely approved the time spent on a page as an essential ranking factor.
If people exit a site with mixed content soon after landing, there is a high chance that Google’s algorithm may demote the site in the SERP rankings.
Want to see your website at the top? Don’t let your competitors outshine you. Take the first step towards dominating search rankings and watch your business grow. Get in touch with us now and let’s make your website a star!
What is a Mixed Content Error?
The web pages are rendered by browsers based on two protocols – HTTP and HTTPS.
A website that follows the HTTPS protocol is far safer than one that uses HTTP. HTTPS-enabled sites are encrypted, thus ensuring authentication, data integrity, secrecy.
However, there are websites that load both HTTPS and HTTP content on the same page and this is called Mixed Content.
Most sites that face mixed content issues have external resources such as images, videos, stylesheets, scripts loaded via the HTTP domain.
Even though the initial request is sent as HTTPS, once the mixed content is rendered in the Google Chrome browser, it shows the site as insecure as there are chances that the HTTP resources may harm the users.
How to Fix Mixed Content Issue?
If you have an HTTPS domain but see the “Not Secure” notification on the Omnibox of the Chrome browser, there is a high chance that your website has Mixed Content.
Step 1: Identify Mixed Content on the Page
If you see the browser notification that says “Insecure content found on the webpage,” go to the source code and check whether you see the “http://” URLs on the page. You can do this by doing a simple CTRL+F on the source code. You can find HTTP URLs with mixed content errors and warnings this way. 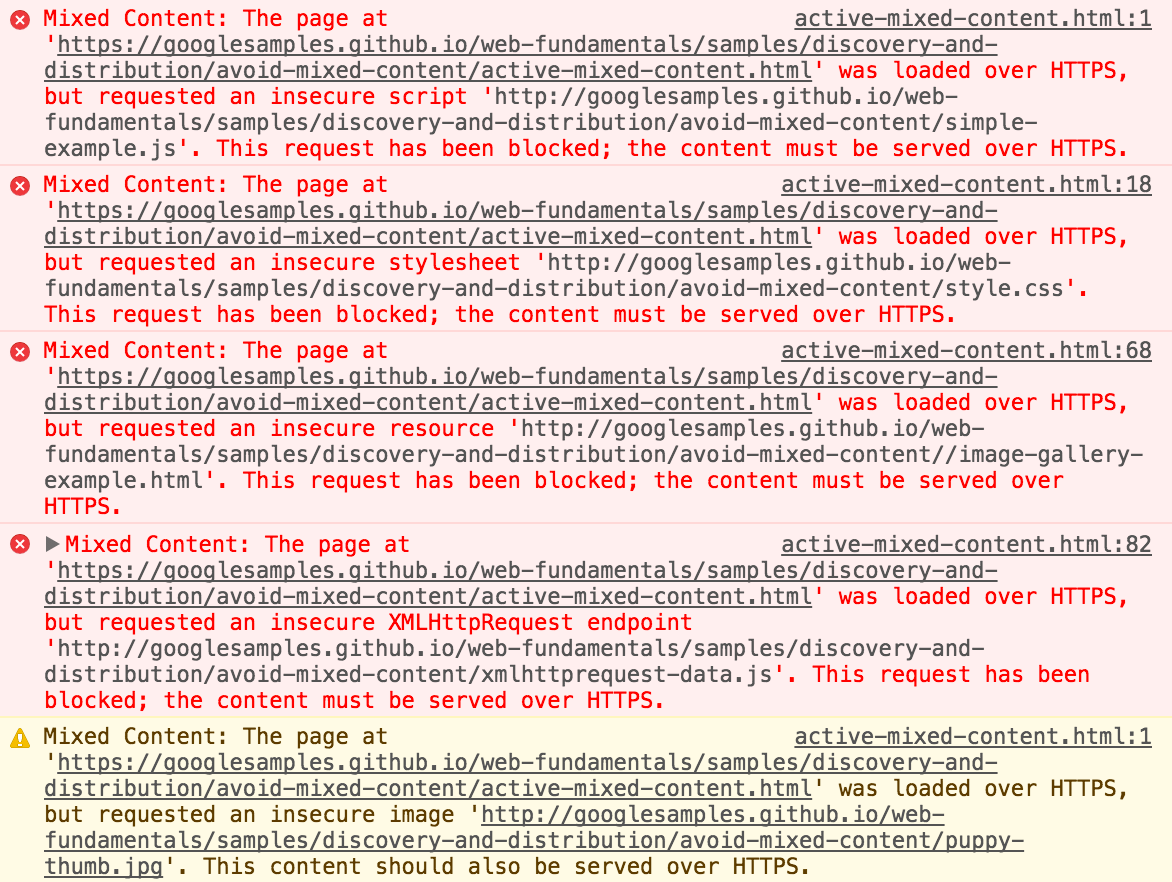
Step 2: Check if the Resource is Available in HTTP and HTTPS
There are chances that the mixed content is available in both HTTP and HTTPS. In such cases, you don’t have to make any changes as the Chrome Browser 79 will auto-upgrade mixed resources to https://, so sites will continue to work.
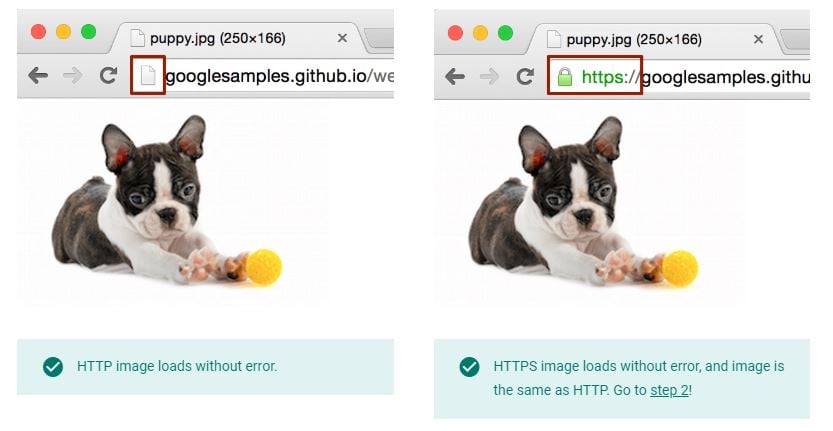
However, if you fail to find the HTTPS version of the same file – “Resource not available over HTTPS”, or if you see a Chrome Notification that says “Certificate warning when attempting to view resource over HTTPS”, you have to consider migrating the resource to HTTPS.
Step 3: Migrating an HTTP Resource to HTTPS
If you find resources that are not in HTTPS or faced warning while accessing, you must consider doing the following:
- Include the same resource from a different host that serves the HTTPS version.
- If your external resource is a downloadable asset, download the same and host it in your HTTPS server.
- If the resource is not integral for rendering the website exclude it altogether.
Step 4: Update the Source File
Once you have uploaded the resource on an HTTPS domain, update the source code with the new HTTPS URL of the resource.
Step 5: Check Whether the Error Has been Resolved.
A Timeline of Mixed Content Warning Rollout?
Starting in December 2019, Google Chrome will start treating websites with mixed content differently. Instead of an overnight exclusion, Google is planning to phase out mixed content with a series of Chrome Updates, says the official announcement.
Phase 1 – The Chrome 79 Update will be rolled out in December 2019 and it will unblock mixed content on specific sites. This chrome version will auto-upgrade HTTP to HTTPS wherever possible. 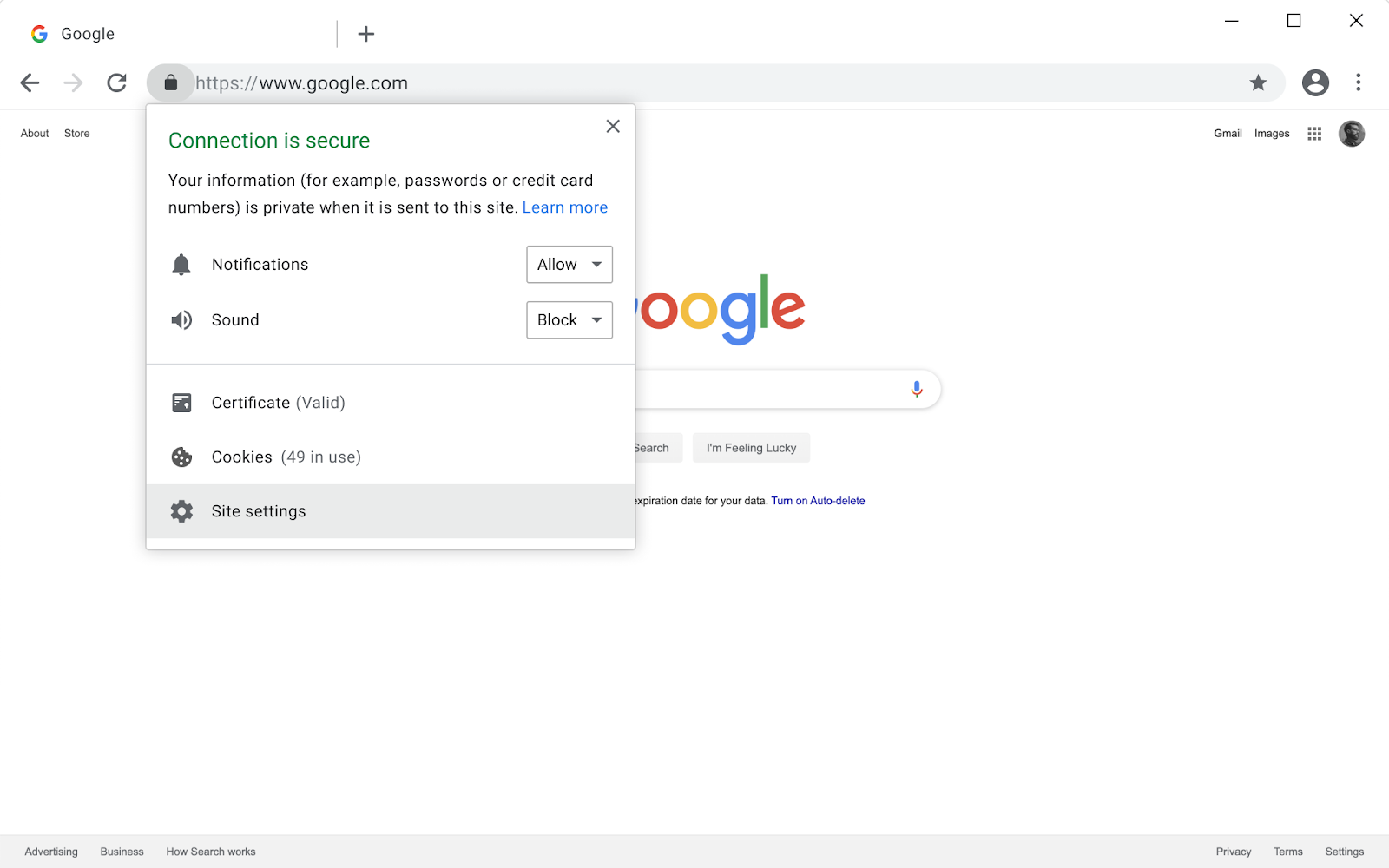
Phase 2: The Chrome 80 update is all set to launch in January 2020. This update brings along HTTPS auto-upgraded features, which will upgrade the unsecured HTTP connection to a more secure HTTPs connection. Taking the Chrome 80 update further, if the content fails to load over an HTTPs connection, then the browser will automatically block it.
![]()
Phase 3: To add further, the mixed image will still be allowed to load in the Chrome 80 update, but it will come with a “ Not Secure” warning by the browser in the Omnibox next to the URL of the website, as shown in the image above. This is expected to prompt users to migrate their images to HTTPs.
Phase 4: The next upgrade, which is the Chrome 81 update, will also come with HTTPs auto-upgraded features. Chrome will block the images that fail to load over an HTTPs connection. As per reports, Chrome 81 update is coming in February 2020.
Examples and Case Studies 2024
A notable case is the e-commerce giant whom we helped recently. Initially, they faced mixed content warnings due to some HTTP-loaded images.
Post-fixing this by updating all resources to HTTPS, the site reported a 20% increase in user engagement and a notable reduction in cart abandonment rates. Of course who trusts a website that Google doesn’t trust!
This change underscored the importance of secure browsing in enhancing user trust and interaction.
Impact of Mixed Content Error on SEO and User Experience
Mixed content error can significantly impact SEO and user experience. Search engines like Google prioritize secure websites, meaning that HTTPS sites often rank higher than their HTTP counterparts.
For users, a warning about insecure content can erode trust and increase bounce rates.
By migrating to HTTPS, websites not only secure their user data but also improve their SERP standings, a crucial factor in today’s competitive digital landscape.
Additional Browser Behaviors
Other major browsers also have specific ways of dealing with mixed content.
For example, Mozilla Firefox blocks certain types of mixed content like active content (scripts) by default, providing an option to load non-secure items.
Similarly, Microsoft Edge and Safari have implemented measures to warn users about potentially insecure content.
Understanding these behaviors is vital for webmasters to ensure a seamless user experience across all browsers, further emphasizing the universal need for HTTPS implementation.
Get Your Free SEO Audit Now!
Enter your email below, and we'll send you a comprehensive SEO report detailing how you can improve your site's visibility and ranking.

You May Also Like
How to Harness First Contentful Paint (FCP) for Faster Page Loading
Did you know that improving site speed by just 1 second can bring 27% more conversions? Every user experience metric that takes you closer to that one–second improvement matters. There’s one metric that can help you showcase an excellent site speed and attract your visitors at the first instance. That is First Contentful Paint (FCP). … How to Harness First Contentful Paint (FCP) for Faster Page Loading
How to Leverage Time To First Byte to Boost Your Page Loading Speed
Do you still find your web page loading sluggishly even after optimizing its page speed? You are probably focusing on the front-end performance of your website. I suggest you pay attention to the backend as well. That’s where page loading begins. A slow Time To First Byte is one such server-side issue that is most … How to Leverage Time To First Byte to Boost Your Page Loading Speed
Do 404 Errors Matter in SEO? Best Practices and Google Insights
404 error pages are pretty common across the web. However, the existence of pages with 404 errors can harm your SEO efforts. Read more to know how.








Comments