25 SEO Myths You Must Ignore in 2024 & Beyond
By: Shreoshe Ghosh | Updated On: December 27, 2023
Table of Contents
Nowadays, there are a lot of tips and tricks about SEO.
However, some of them are beneficial while some are entirely misleading.
Some of the SEO tips are so common that they blur the line between myth and reality.
Without an in-depth understanding of SEO, it is hard to tell the difference between real SEO and its myths.
But what is the reason behind the existence of these myths?
Well, no one COMPLETELY understands how search engines work, which is why SEO requires a lot of trial, error, and guesswork.
It is challenging to try and implement every SEO tip you come across, so certain SEO myths become prevalent.
Most SEO myths can be debunked with a bit of common sense and considerations.
For example, whenever you plan to implement an SEO tip, ask yourself how it will benefit the search engine or the end-users?
If the SEO tip is nothing more than a myth, you won’t be able to answer the above questions satisfactorily.
Let’s look at the top SEO myths that exist in 2024.
1. The Google SandBox
It is believed that Google will automatically suppress the ranking of new websites in the organic results for some time, post which they’ll rank more freely.
Google has confirmed on social media that there is no such thing as SandBox.
However, there does seem to be a certain amount of time that Google takes to understand and rank pages belonging to a new site.
This mimics a sandbox that might drive people into believing it is a true phenomenon.
2. Duplicate Content Penalty
The idea that your site will be penalized by Google if found copying content from another site is a popular myth.
This is where you need to understand the difference between algorithmic suppression and manual action.
A manual action or penalty leads to a webpage being removed from Google’s index.
The webmaster will be notified about the same on Google Search Console.
Manual penalties are levied when human reviewers at Google find your site violating Google Webmaster guidelines.
An algorithmic suppression occurs when your page cannot rank due to being caught by a filter from an algorithm.
Copying content from another site doesn’t mean you can outrank it. Google will determine the original content to be more relevant than the copied content on your site.
As there is no benefit of showing the same content in the search results, the web page that contains the copied content gets suppressed.
This is not a penalty, rather the course of action of an algorithm.
Although there are content-related manual actions, copying content from another site will not trigger them.
However, such a practice can land you into legal trouble of copyright infringement and make your site less valuable to your users.
3. PPC Advertising Helps Ranking
The idea that Google will favor sites that invest money in paid advertising through its pay-per-click advertising program is a big myth.
Google’s algorithm for ranking websites in the organic search results is entirely different from the one used to determine Google ad placements.
Running paid advertising campaigns on Google alongside SEO for your site can be beneficial for other reasons, but it has no direct effect on your rankings.
4. Domain Age is a Ranking Factor
Many webmasters believe that because a website has been around for a long time and is ranking well, age must be a ranking factor.
Google has debunked such a myth several times. Recently in July 2019, John Mueller replied to a tweet saying that domain age is one of the 200 ranking factors, saying “domain age helps nothing.”
Older websites only get more time to do things well. This is the truth behind this myth.
A website that has been around for 10 years must have acquired a high volume of backlinks to its prime pages, and a website that’s half its age can’t compete with that.
5. Tabbed Content Affects Rankings
It is another common belief that Google will not give much value to the content that is not viewable in the first load of the page.
However, Google has denied any such thing because if the content is viewable in HTML, there is no reason the content would be devalued just because it doesn’t appear to the users during the first load.
This isn’t a case of cloaking since Google can fetch the content easily.
6. Google Uses Google Analytics Data in Rankings
A common belief is that Google takes data from Google Analytics to rank websites as a part of its ranking algorithm.
It is a common fear in webmasters that if their Google Analytics data is not up to the mark, such as a high bounce rate or low time spent on the page, Google will perceive their site as low-quality and will affect its rankings.
In reality, using Google Analytics data as a ranking factor is hard to consider.
You can use filters to manipulate the data that makes your site seem like it was performing in a certain way that can be quite different from reality.
For example, a high bounce rate is an indication that your site isn’t user-friendly or lacks quality content.
However, what it could really mean is that your content is quickly digestible.
The metrics on Google Analytics give you clues why your site might not be ranking well, but they don’t necessarily need to be the cause.
7. Google Cares About Domain Authority
Google uses the PageRank algorithm to measure the importance of a webpage.
Google used to display a page’s PageRank score on its toolbar, a number between 0-10.
Google stopped displaying PageRank in the toolbar in 2013, and in 2016, Google confirmed that the PageRank toolbar metric wouldn’t be used in the future.
Generally, SEOs correlate the ranking power of a website with its backlink profile. This metric is also known as Domain Authority (DA).
In the absence of the PageRank metric, many third-party metrics came into play, such as:
- Moz’s Domain Authority and Page Authority scores.
- Majestic’s Trust Flow and Citation Flow.
- Ahrefs’ Domain Rating and URL Rating.
These scores are now used by some webmasters to determine the value of a page. However, they cannot entirely reflect accurately how search engines value a page.
Gary Illyes has debunked the myth in response to a tweet with “we don’t really have overall domain authority.”
8. Longer Content is Better
You must have heard it before that longer content performs better.
More words written about a topic make it more authoritative than your competitors. It is knowledge shared on SEO forums without much evidence.
Many studies have been carried out over the years that throw light on the top-ranking pages in Google.
One of them says that the average word-count for the top ten pages on the search engine is 1450 words.
This can lead many people to believe that in order to obtain any of the top ten positions on Google, your content should be at least 1500 words.
However, that’s not what the study meant. Just because for a particular study, the top-ranking pages happened to have more words than the pages at position 11 and beyond doesn’t make word count a ranking factor.
John Mueller confirmed the same in a tweet.

9. LSI Keywords Will Help You Rank
LSI refers to “latent semantic indexing.”
LSI keywords help search engines better understand a page content by adding context to the target keyword.
Words differ depending on their context. For example, the word “right” can have a different meaning when paired with the words “left” and “wrong” separately.
Humans can understand the context between different words much quicker than machines, which is why LSI is a massive step towards the ability of a machine to understand the text.
However, the SEO community believes that LSI keywords will boost rankings for words that aren’t expressed well in the text.
This isn’t true since Google has gone beyond LSI keywords to understand text, like introducing the BERT update.
10. SEO Takes 3 Months
It takes three months for SEO to show results is yet another popular myth that has no solid evidence.
It is fair to say that SEO efforts take time to show results, and 90 days is a reasonable time to observe whether your SEO efforts are showing positive or negative results.
However, it is still not enough to conclude whether the effort is 100% profitable for your site.
If your market competition is low, and you target niche terms, Google might take only a recrawl to show ranking changes.
A competitive keyword will take much longer to see improvement in rankings.
Several factors can influence your site SEO, such as Bing, Yandex, and Baidu search engines are easier to rank for than Google.
A minor tweak to a page title can increase the click-through-rate (CTR). That could happen if the search engine spiders recrawl the page on the same day.
To reach the first page ranking on Google may take a lot of time. Hence, measuring SEO efforts in a 3-month timeline isn’t appropriate.
11. Bounce Rate is a Ranking Factor
Bounce rate is the measure of the amount of visits on your website that result in no interaction beyond landing on the page.
It can be measured using Google Analytics.
Some SEOs believe that bounce rate is a ranking factor because it is a measure of quality.
There can be several reasons why visitors may want to leave a page as soon as they land in. They might have read all the information present on the page and left it to contact the business. In that case, the bounce has actually proved beneficial for the concerned business.
It could also happen that people bounce from your page due to the poor quality of the content on your site.
Therefore, bounce rate cannot be considered as a quality indicator.
Instead, Pogo-sticking, or a visitor clicking on a search result and then returning to the SERPs immediately, would be a more reliable indicator of the landing page’s quality.
It suggests that the page’s content was not what the user wanted, so they have returned to the search results to browse another page or re-search.
12. It is All About Backlinks
There’s no doubt backlinks are essential for SEO, but how much importance they actually have is something to think about.
Some will argue it is one of the many SEO tactics that help improve the site ranking, while others may say it is the only thing that matters in SEO.
Back in the day, you could build links wherever you wanted, such as online forums, directories and more.
However, with Google changing its algorithm often, link building is no longer an easy task.
Google now only rewards relevant and high-quality links and penalizes spammy links.
On mobile devices, you can often see dozens of results before you reach your first organic result.
Relevant backlinks do help with ranking, but you cannot rely on them solely.
Optimized content, images, video, and schema can help you maximize your SERP visibility.
You need to combine these optimization techniques to convert more visitors and improve your site ranking.
13. Keywords in URL is Important
Adding keywords in the URL doesn’t provide much value now.
John Mueller has cleared this many times that having keywords in the URL is a minor ranking factor.
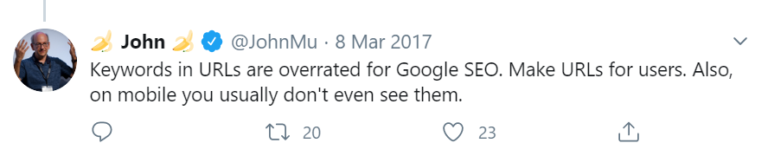
If you are planning to rewrite your URLs to include keywords in them, you may do more harm than good.
14. Website Migrations Are All About Redirects
A common suggestion that you receive from SEOs is if you are migrating your website, you need to redirect any URLs you are changing.
In reality, website migration is one of the most complicated procedures in SEO.
Website migration can refer to a change in website layout, CMS, or domain.
You need to consider several things to maintain your website ranking and traffic even after the migration.
You need to take care that the tracking hasn’t been lost, the same content targeting is maintained and more.
Redirecting URL changes is an integral part of website migration but it doesn’t make it the most important thing to worry about.
15. Well-Known Websites Will Always Outrank Unknown Websites
Since larger brands have more resources than smaller brands, they can invest more money in SEO.
Some SEOs believe Google favors big brands, but it says otherwise.
In 2009, Google released the “Vince” update, which had a massive impact on how brands were treated on SERPs.
Brands that were well known offline saw an increase in ranking for broad competitive keywords.
Big brands are also often more authoritative than smaller brands, however, that doesn’t mean smaller brands cannot win.
Targeting long-tail keywords or establishing local presence are some steps that can help smaller brands be more relevant in search results than bigger ones.
Although outranking bigger brands is tough, it isn’t entirely impossible.
16. Your Page Needs to Include ‘Near Me’ to Rank Well for Local SEO
When a searcher is looking for something with a location intent, the search engine will return results taking that particular place or physical location into consideration.
You’ll get Google Maps results as well organic listing with Google search.
So, people looking for “dentist near me” will be served with the details of dentists near their location by detecting their location data.
Without it, it is impossible to know what your “near me” location would be.
The “near me” element of the search is less about the keyword but more about the intent.
Therefore, you do not need to include “near me” in your keywords to rank for local SEO.
Instead, you should strive to be relevant to the location the searcher is in.
17. Better Content Means Better Rankings
Better content means better ranking is a prevalent myth without proper evidence.
Content quality is a subjective consideration. If your content ranks below your competitors, it could be due to many reasons.
You might not meet the search intent as perfectly as your competitors or you must have over-optimized your content and compromised with its quality.
Content is one of the factors that influence ranking algorithms. It could be easily affected due to other factors like the site’s technical performance or the lack of local relevance.
18. You Must Blog Every Day
As per a 2011 Google algo update, fresh results are rewarded in the SERPs because fresher results bring more content accuracy.
While this algorithm update doesn’t mean newer content will always outrank older ones, it is up to Google whether a particular query deserves freshness or not.
If it does, the age of the content becomes an important ranking factor. That doesn’t mean you will create new content just to outrank your competitors.
It won’t necessarily work that way.
If the query doesn’t change the fact/deserve freshness, writing new content won’t help you outrank older content on the same topic.
For example, a search like “What is the Beatles debut album?” doesn’t require freshness in results.
If you are writing content every day, thinking it will help you rank on top and keep your website fresh, you’re mistaken.
It is advisable to write less frequently but ensure that the content is informative, authoritative and valuable.
19. You Can Optimize Copy Only Once
An SEO-optimized copy is a piece of content that is written to rank for related search queries.
Usually, when you write such a copy after extensive research and see it performing well, you leave it to that.
Unfortunately, over time, the keywords to target may change along with what users might look for in your content.
The search engine may also prefer some other content over you as time passes if they find it to be more relevant than yours.
Therefore, to ensure that your SEO-optimized copy is always at the top of SERPs, you need to keep optimizing your copy by updating the content and keywords from time to time.
20. There Is a Right Way to Do SEO
There are some core rules in SEO, but there is no rulebook on how to do SEO for a website.
SEO results from different strategies discovered or tried and tested for personal experiences and conclusions.
Every industry is different, so a strategy that might work for one industry might not work the same way for others.
Therefore, before giving any SEO advice or concluding SEO results, see whether it is working only for your site or across websites.
21. Links Must Pass a Minimum DA or Other Score to Pass Value.
Webmasters often rely on third-party metrics such as Domain Authority, Domain Rating, or Citation Flow when evaluating link opportunities.
However, it is important to note that these numbers will vary from source to source, so you should never blindly believe them.
Google does not just use page rank scores to decide how to rank websites or treat links from them.
Even if a link comes from a low-scoring website, it could still give you backlink value and drive potential customers.
Common sense should dictate whether or not you are going to pursue a site for links.
If a website logically links to you for reasons that are not solely SEO-driven or commercial in nature, those links are worth taking, even if they do happen to have a lower score.
22. You Should Only Accept Links From Relevant Websites
In a perfect world, other websites within your niche would link to you – it’s only logical. In most instances, they are your competitors who are not inclined to link back.
Achieving high-quality links can prove difficult in fiercely competitive industries, but stretching out the relevance gap when searching for opportunities will provide good long-term results.
Doing so will significantly increase the quantity and quality of link prospects, helping you find link-earning opportunities you would otherwise miss.
This can be accomplished by developing a robust content plan with appealing links for these audiences that offer something worthy of sharing.
23. It’s Worthwhile to Rely on Guest Blogging and Link Networks
If you currently receive links from guest blogging, buying links, or participating in other actions that violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines, you should stop doing so immediately.
For many years, Google has been clear about this—guest blogging and link buying as strategies violate their webmaster guidelines.
Although these methods can provide a quick boost, they only last for a while, and once Google knows about them, your website reputation may never recover.
Google has been ignoring these links in your backlink profile for the past couple of years, which is good news.
However, penalties are still imposed in some instances, so it’s better to be safe than sorry.
24. Internal Linking isn’t Important
A lot of webmasters overlook internal linking optimization. Internal linking optimization is one of the most effective ways to increase your SERP presence, especially for mid and long-tail keywords.
Linking internally allows you to change your anchor text from page to page, raising their ranking for various search terms.
It also lets you control where links are located across your site, giving visitors another way to navigate them.
25. Link Building is Dead
John Mueller suggested in a recent podcast that links may become less important as time goes on.
One of the things which historically sets Google apart from every other search engine is its reliance on link data to determine a site’s rank.
In recent years though, Page 1 of Google has looked very different compared to 10 years ago.
As mentioned before, this requires additional optimization opportunities that links alone can’t take care of.
Google discourages people from constructing artificial links.
Research has shown that, over time, good-quality backlinks are more effective than low-quality ones when it comes to search engine rankings.
Ranking a website for high-value keywords within a competitive vertical without strategic links will likely remain challenging for many years to come.
Which of these SEO myths did you believe to be true? Let us know in the comments below.
How Do SEO Myths Originate?
Before we discuss the SEO myths, let’s try understanding where these myths originate from.
Untested SEO Tips
SEO myths arise out of untested handed-down wisdom. Due to this, something that barely has any impact on the site’s ranking might be considered very important.
Minor Factors Taken Too Seriously
Some SEO factors may have a minor effect on a website but are given too much importance.
Overdoing these minor optimization, such as repeating keywords in your content, can hurt your site rankings.
Outdated Practices
Another reason why so many SEO myths still exist is due to the outdated SEO practices that some people still consider essential.
As Google comes up with new algorithmic changes, certain SEO practices that once worked well for a website don’t hold importance anymore.
Practicing such outdated SEO practices can negatively affect your website.
Not Understanding Google Updates Well
Sometimes, Google’s announcements are not very straightforward, which prevents people from decoding their exact meanings.
This can lead to multiple interpretations, none of which resemble what the search engine giant actually meant.
If you’ve been in such a situation, it is recommended that you discuss it with your fellow webmasters before drawing conclusions.
When Can An SEO Technique Appear to Be a Myth?
Sometimes, an SEO technique that has worked for a website might not work with the same effectiveness on another site, which means the result varies from website to website.
In such a scenario, the SEO technique may be written off as a myth simply because it failed to work effectively on a website.
It should be noted that every website is different in terms of the niche they belong to, the audience it is serving, the competitors it has, and the technology it is using.
Copying an SEO technique from a website just because it brought it some success is not recommended.
This is applicable even if you are following your competitors’ techniques. What worked for them might not work for you due to several factors involved.
Another common scenario is an inappropriate connection between an SEO activity and a rise in your organic search traffic.
Just because one of your SEO parameters improved around the same time you implemented a new SEO strategy doesn’t make it accountable.
There could be many reasons why you’re suddenly seeing a spike in your page’s click-through- rate (CTR).
However, many SEOs tend to believe otherwise and start believing that the new SEO technique has helped them see the positive change in their site analytics.
Debunking SEO Myths
If you’ve wasted a lot of time, money and hope on SEO myths, it’s time to debunk them and avoid making wrong conclusions.
Here’s how:
The best way to avoid falling for SEO myths is to test them in the first place.
If you’ve been advised to follow a specific page structure to get better conversions, try it out with one or two of your webpages and analyze the difference.
If you don’t see any satisfactory results, don’t implement them for the rest of your webpages.
Is Google Just Testing?
There are times when the SEO community starts buzzing the moment they notice a change in the way Google displays search results.
These changes are often tested by Google before they are rolled out to the public officially.
However, the moment it gets to the notice of some webmasters, they start looking for ways to optimize it.
Similar instances happened when Google was testing favicons in search results, and many webmasters began publishing articles on the importance of favicons in attracting users to your search result.
However, Google changed it back before people could even determine how it would affect the CTR.
Therefore, before jumping to conclusions because of new features tested by Google, you should wait for a while to see whether those changes are permanent and only then start optimizing for it.
Google might roll back the change, but your site’s performance gets affected negatively due to your site’s recent changes.
Get Your Free SEO Audit Now!
Enter your email below, and we'll send you a comprehensive SEO report detailing how you can improve your site's visibility and ranking.

You May Also Like
Turnaround Time (TAT) for SEO Projects: How Agencies Set Expectations
As an agency owner, the key to delivering a faster ROI for your clients is promptly implementing the proper SEO strategies. However, managing hundreds of client websites simultaneously means each client expects rapid results. That’s why your SEO agency must set clear expectations about turnaround time (TAT) with your clients, ensuring they understand the process … Turnaround Time (TAT) for SEO Projects: How Agencies Set Expectations
6 SEO Pricing Models for Agency Owners
When it comes to SEO service pricing, it can be difficult to know what is a fair price and what is too much. Read this blog to know more.
What’s a Good Click-through Rate?
Checkout some of the most effective ways to improve the CTR (Click Through Rate) which is one of the hidden search engine ranking factors.









Comments
2 Comments
Thanks for sharing this informative post with the readers and clearing all the misconception about digital marketing. I would like to share it with my friends too as this is helpful to them as well. Keep posting such helpful posts.
Sai Digbijay Patnaik, this post is really an eye-opener that shows how foolish people are to believe in such digital marketing myths. I really believed that greater the traffic, greater the success rate of the website. It is nice that you have averted this misconception through this post. Great share!